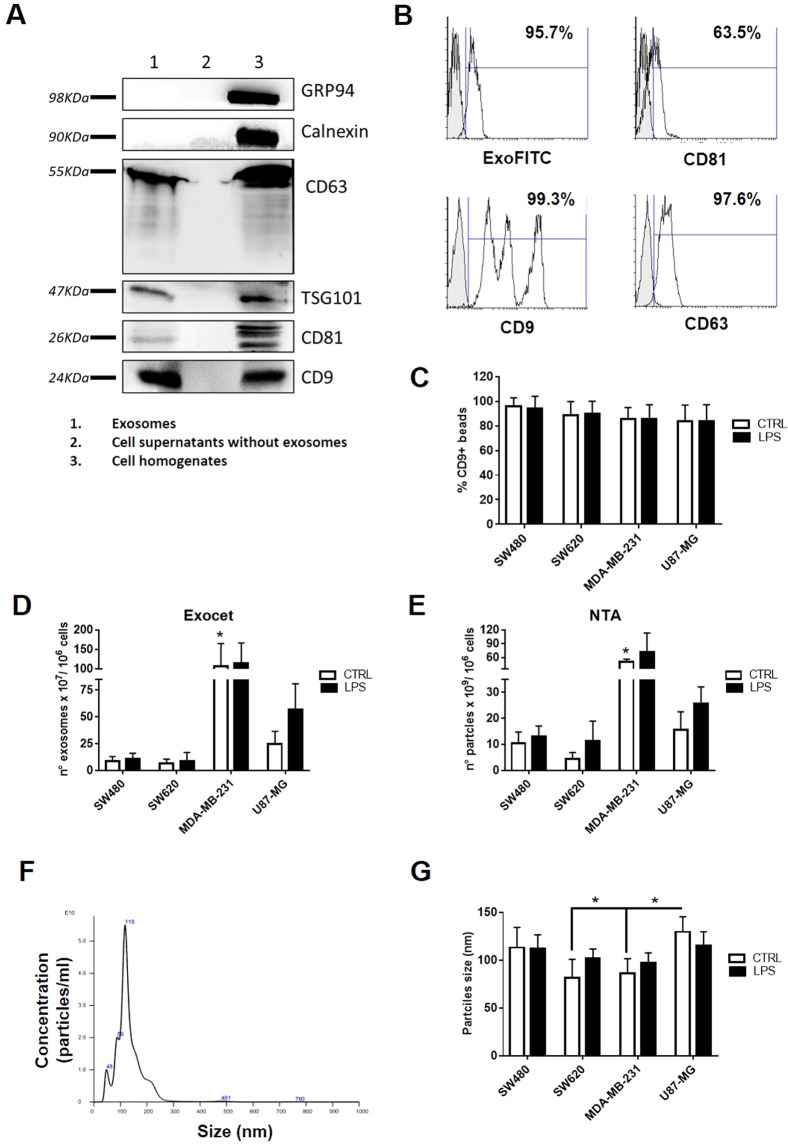
Figure 2.
Characterization of exosomes released by tumor cells. (A) Immunoblot analysis of SW480-derived exosomes, Exoquick-derived supernatants and cells homogenates probed for the indicated proteins. (B) Exosomes were coupled to ExoFlow beads, stained with ExoFITC dye or specific monoclonal antibody for CD81, CD9, and CD63 and analyzed by flow cytometry. The antibodies (white peak) were compared with their appropriate isotype control (grey peak). Histograms from one representative experiment are shown. (C) The histogram represents the percentages of CD9-positive beads bound to exosomes released by unstimulated (CTRL, white column) or LPS-activated cells (LPS, black column). Data are shown as mean (n = 4) ± SD. (D) The number of exosomes was estimated measuring the enzymatic activity of the exosomal AChE enzyme by Exocet kit (D) or by nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA) by LM10 Nanosight. (E) Data are shown as mean (n = 8) ± SD. *P < 0.05 compared to SW480- SW620 and U87-MG-derived exosomes. (F,G) The particles size distribution was evaluated by Nanosight and a representative graph of frequency size distribution of SW480-derived exosomes is shown. Data are shown as mean (n = 8) ± SD. *P < 0.05.