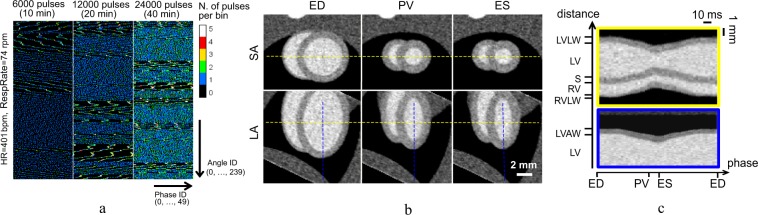
Figure 3.
(a) 2D histograms showing the distribution of the X-ray pulses on the phase/angle diagram for the simulated acquisition of the dynamic phantom. Histograms are binned in 50 cardiac phase bins and 240 angular bins. Dark areas show missing data due to transitory coherence between the cardiac motion and the X-ray pulse sequence. (b) Reoriented short-axis and long-axis images of the mouse heart (only three of the 50 reconstructed phases are shown) obtained by iterative reconstruction from the sequence of 12000 pulses. (c) M-mode-like image of the reoriented heart, obtained along the dashed lines shown in (b) for all the 50 reconstructed time frames. For all images, the voxel size is 100 μm and the temporal binning (frame duration) is 3 ms, calculated as the mean R-R interval divided by the number of reconstructed frames per cycle. ED: end-diastole; PV: peak myocardial velocity; ES: end-systole; SA: short axis; LA: long axis; LV: left ventricle; LVLW: left ventricle lateral wall; LVAW: left ventricle apical wall; RV: right ventricle; RVLW: right ventricle lateral wall; S: septum. FBP: filtered backprojection; SIRT: simultaneous iterative reconstruction technique.