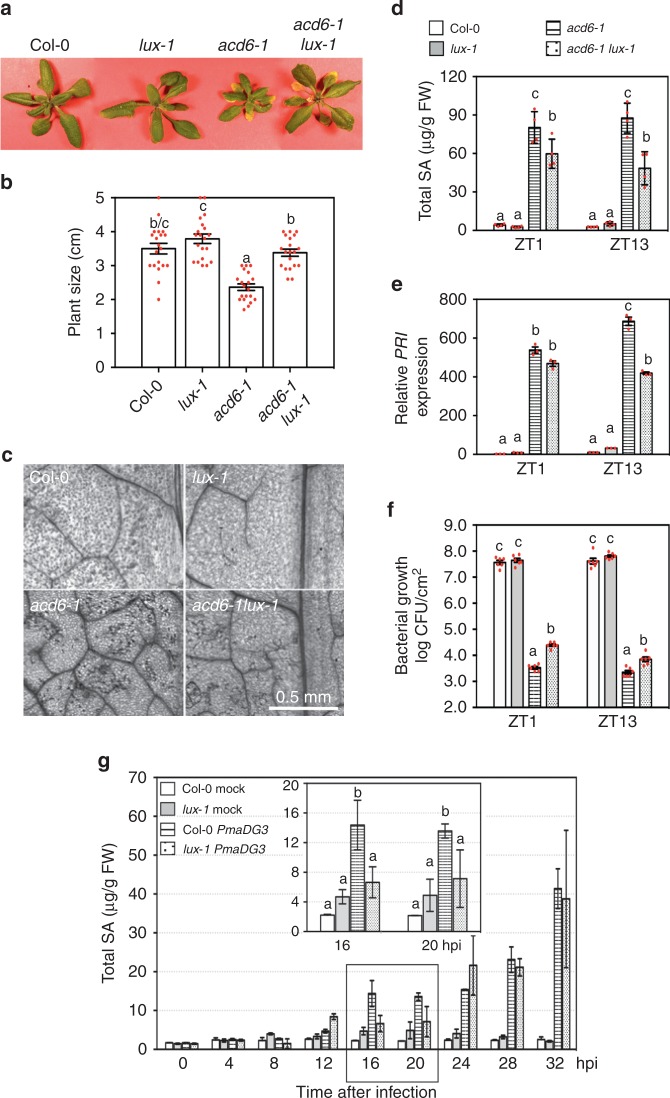
Fig. 1.
The lux-1 mutation suppresses salicylic acid (SA)-mediated defense. a Phenotypes of 25-day-old plants. b Average size of 25-day-old plants. Plants were measured for the largest distance between tips of two rosette leaves (n = 20). c Cell death staining of the fifth to seventh leaves of plants. d SA quantification. Whole plants were collected at ZT1 or ZT13 for SA extraction followed by high-performance liquid chromatography measurement (n = 4 from two independent experiments). e Expression of PR1. Whole plants of each genotype were collected at ZT1 or ZT13 for RNA extraction followed by quantitative reverse transcriptase–PCR (qRT-PCR) analysis (n = 3). f Bacterial growth. The fourth to sixth leaves of each genotype were infiltrated with PmaDG3 (OD = 0.0001) at ZT1 or ZT13 and assessed for bacterial counts at 3 dpi (n = 6). g SA quantification with plants infected by PmaDG3. The fourth to sixth leaves of each genotype were infiltrated with PmaDG3 (OD = 0.01) or the mock solution at ZT1 and collected at the indicated time points for SA analysis (n = 2). Data represent mean ± SD in d, e, g and mean ± SEM for b, f. Statistical analysis was performed with one-way analysis of variance with post hoc Tukey honestly significant difference test. Different letters in b, d–g indicate significant difference among the samples at the same time point (P < 0.05). These experiments were repeated three times with similar results