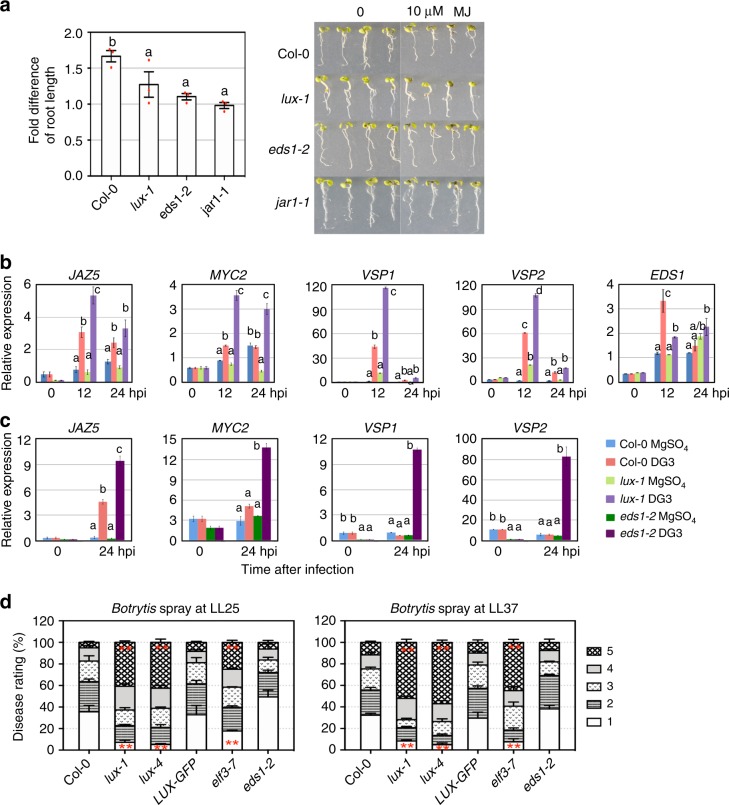
Fig. 4.
Mutations in LUX and EDS1 affect jasmonic acid response and signaling. a Root length inhibition with methyl jasmonate (MJ) treatment. The fold difference of seedling root length (left) was calculated as the ratio of seedling root length with water treatment/seedling root length with 10 µM MJ treatment. The MJ-insensitive mutant jar1-168 was used as a negative control. Data (left) represent mean ± SEM of three independent experiments (n = 6 seedlings per genotype/treatment in each experiment). Photographs of the seedlings (right) are from one representative experiment. b Quantitative reverse transcriptase–PCR (qRT-PCR) analysis of gene expression affected by lux-1 upon PmaDG3 infection (n = 2). c qRT-PCR analysis of gene expression affected by eds1-2 upon PmaDG3 infection (n = 2). d Disease rating of Botrytis-infected leaves. Plants were sprayed with Botrytis (2 × 105 spores/ml) 25 or 37 h after onset of LL and the fourth to sixth leaves of each genotype were scored for disease symptoms 4 dpi (121 or 133 h after onset of LL) using the following rating scale: 1 = no lesion or small rare lesions; 2 = lesions on 10–30% of a leaf; 3 = lesions on 30–50% of a leaf; 4 = lesions on 50–70% of a leaf; 5 = lesions on >70% of a leaf. Data (left) represent mean ± SEM of three independent experiments (n = 30 leaves per genotype in each experiment). Statistical analysis was performed with one-way analysis of variance with post hoc Tukey honestly significant difference test. For a–c, different letters indicate significant difference among the samples at the same time point. For d, asterisks indicate significant difference in the same disease scale category between Col-0 and other genotypes. The experiments in b, c were repeated two times and similar results were obtained