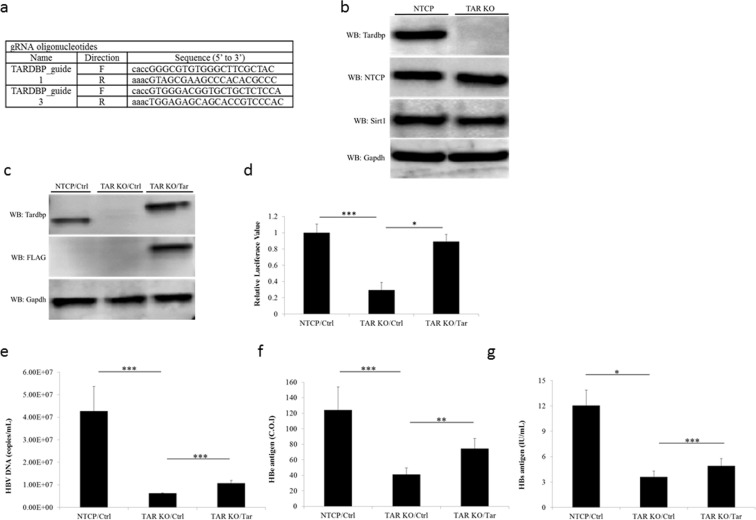
Figure 4.
Establishment of TARDBP-knockout (KO) cells by a CRISPR/Cas9 system. (a) A TARDBP-deficient NTCP-HepG2 cell line (TARDBP KO) was established by the CRISPR/Cas9 system using the two RNA guide sequences shown. (b) Western blot analysis of the NTCP-HepG2 parent cell and the TARDBP knockout NTCP-HepG2 cell line using the antibodies against NTCP, TARDBP, SIRT1 and the control GAPDH is shown. (c) A TARDBP plasmid was transfected into the KO cells for exogenous protein expression. The expression was confirmed by western blotting using the anti-TARDBP and anti-FLAG antibodies. (d) NTCP-HepG2 parent cell, TARDBP KO and TARDBP KO cells complemented with exogenous TARDBP were transfected with the pGL3-CP plasmid for comparison of the core promoter activities. Cell lysates were harvested after 48 hours for the dual luciferase assay as in Fig. 3e. (e,f,g) HBV infection was carried out in the three cells treated as in (c) for 12 days, similar to the experiment in Fig. 1. The supernatants were harvested at the end of the infection period for measurement of extracellular HBV DNA, HBe antigen and HBs antigen levels, respectively. The data is shown as the mean ± SD, *P < 0.05 **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.