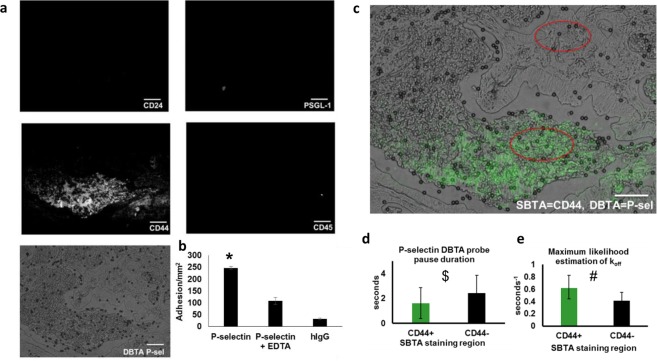
Figure 5.
Adhesion in regions not detected by SBTA implies the presence of potentially distinct P-selectin ligands. (a) In the same regions of tissue that displayed P-selectin DBTA probe adhesion (Supplementary Video S11), examination of serial sections with SBTA (immunostaining) revealed no detectable levels of CD24 or PSGL-1 epitopes. CD44 expression was detected, but not all regions displaying specific reactivity with the P-selectin DBTA probes used in DBTA were recognized with the CD44 antibody in SBTA. Follow-up CD45 SBTA ruled out the possibility of DBTA probe interaction with infiltrated leukocytes, in agreement with the lack of PSGL-1 detection. (b) P-selectin DBTA probes specifically adhered to the tissue, with respect to the negative controls. Data shown are mean adhesion ± SD of three technical replicates and are representative of independent experiments conducted on tissue sections from >3 independent cases of colon cancer. *P < 0.0025 compared to all other conditions. (c) A direct comparison using a composite image of P-selectin DBTA probe adhesion (microspheres) and SBTA detection of CD44 (green pseudocolor) on colon adenocarcinoma tissue. Red ellipses indicate regions analyzed in (d,e). (d) Characterization of the adhesion of P-selectin DBTA probes to functional selectin ligands that were and were not detected with SBTA using CD44 antibody in (a). Data shown are mean pause duration ± SD of 30 separate pauses (n = 30). $P = 0.0068. (e) Data shown represent the estimation of P-selectin DBTA probe koff using the method of maximum likelihood from 30 separate pauses (n = 30). Error bars represent 95% CI. #Mann-Whitney U-value = 1152.5 (equivalent to P < 0.001 for t-test for normal distribution). All probes were perfused at 500,000 probes/mL and 0.50 dyne/cm2. Specificity of interaction was confirmed using 10 mM EDTA and hIgG DBTA probes as negative controls. Scale bar = 100 µm. These results imply the presence of potentially distinct P-selectin ligands in the tissue sections.