Table 1.
Comparison of electrophysiological parameters of dopaminergic neurons in the SNc and VTA.
| Electrophysiological parameters | SNc (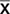 ± SEM) ± SEM) |
VTA (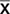 ± SEM) ± SEM) |
Selected references |
|---|---|---|---|
| Body size (μm2) | 176.29 ± 5.84 | 113.18 ± 3.57 | Krashia et al., 2017 |
| Rm (MΩ) | 227 ± 10 | 697 ± 99 | Krashia et al., 2017 |
| Cm (pF) | 57 ± 2 | 44 ± 4 | Krashia et al., 2017 |
| Sag (mV) | 37.3 ± 0.72 | 31.0 ± 1.72 | Neuhoff et al., 2002 |
| Ih (pA) | 299 ± 14 | 45 ± 9 | Krashia et al., 2017 |
| Firing frequency (Hz) | 2.1 ± 0.2 | 1.5 ± 0.1 | Werkman et al., 2001 |
| Significantly inhibited after pharmacologically blocking Ih | Negligible | Neuhoff et al., 2002; Krashia et al., 2017 | |
| EPSP | Obviously enhanced after pharmacologically blocking Ih | Negligible | Masi et al., 2013 |
| IPSP | Significantly inhibited after pharmacologically blocking Ih | Negligible | Masi et al., 2013 |
| SCR | Remarkably activated after pharmacologically blocking Ih | Negligible | Carbone et al., 2017 |
Rm, membrane resistance; Cm, capacitance values; EPSP, excitatory post-synaptic potential; IPSP, inhibitory post-synaptic potential; SCR, somatic calcium response.
