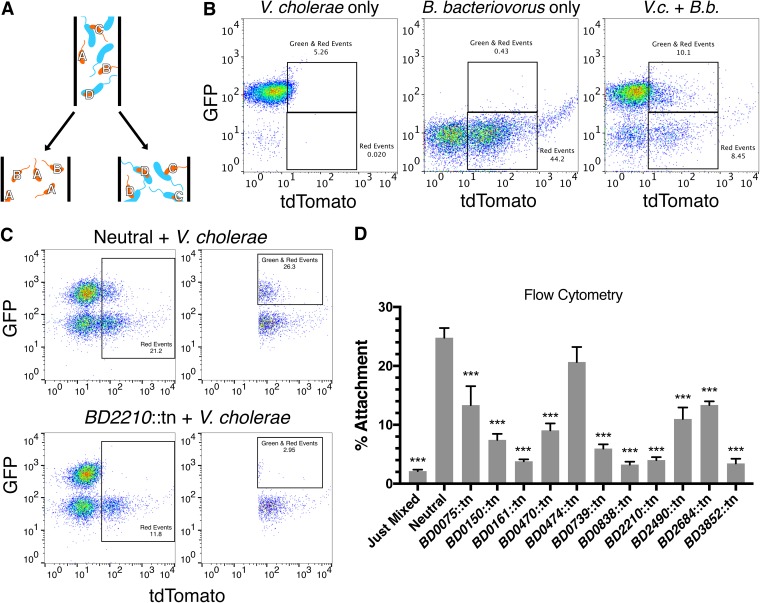
FIG 2.
Identification of B. bacteriovorus mutants with attachment defects by Tn-FACSeq. (A) Schematic of the Tn-FACSeq screen. Following a 3-h infection, red fluorescent B. bacteriovorus are sorted into two pools based on whether they associate with green fluorescent V. cholerae or not. In this example, strains A and B do not attach, while strains C and D do. (B) Example gating strategy used to sort B. bacteriovorus by Tn-FACSeq. V.c., V. cholerae; B.b., B. bacteriovorus. (C) Gating strategy for flow cytometry-based validation of attachment-defective mutants identified in Tn-FACSeq. The left panels gate all red events, and the right panels gate all events that are red and green from the same experiment. (D) Quantification of the flow cytometry results in panel C. The average attachment percentage and standard errors of the mean (SEM) for three to four biological replicates are shown. Significance was determined by comparing each strain’s attachment percentage to that of the neutral control. ***, P < 0.001 (ANOVA and Dunnett’s multiple-comparison test).