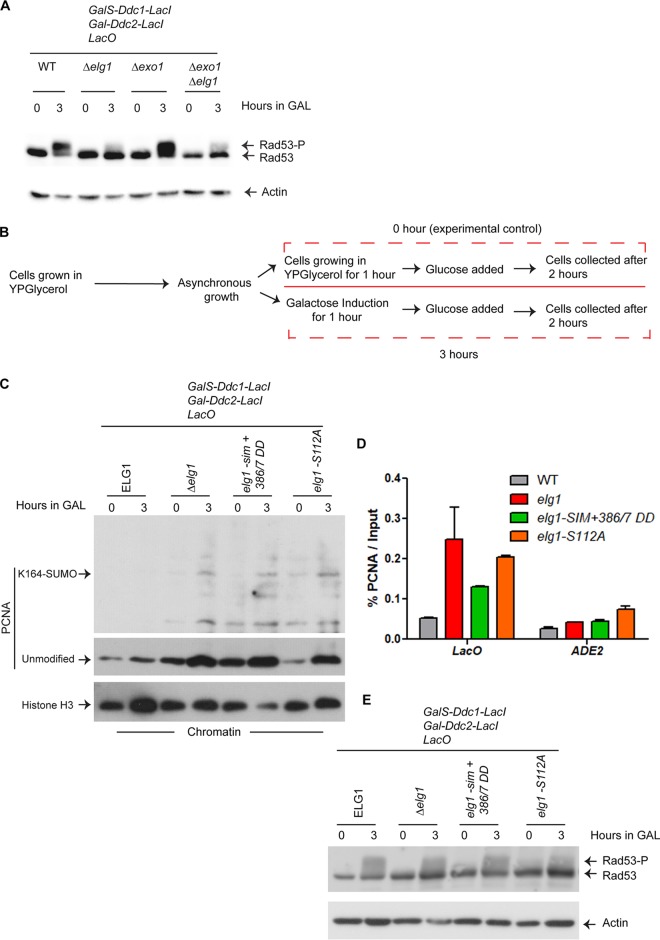
FIG 5.
Accumulated Lac operator site-PCNA impedes Rad53 phosphorylation. (A) Exo1 is not required to activate Rad53 in the DNA damage checkpoint. The checkpoint induction experiments were carried out with WT, Δelg1, Δexo1, Δexo1 Δelg1 to detect phosphorylation of Rad53. Actin was used as a loading control. (B) The schematic diagram represents the experimental regime for Fig. 5C. C. A Western blot of chromatin fractionation assay-samples detects the PCNA level in the indicated strains (ELG1, Δelg1, elg1-sim + 386/7 DD, and elg1-S112A). The histone H3 was used as a chromatin-bound control and also served as a loading control. (D) The checkpoint induction experiments, as described in Fig. 2B, were carried out with Fig. 5C cells, and PCNA was pulled down using anti-PCNA antibody. The histograms of chromatin immunoprecipitated PCNA represents the accumulation level of PCNA at the LacO array in WT and elg1 mutants. ADE2 amplification was the experimental control. At least three biological repeats were carried out; error bars represent standard errors of the means (SEM). One-way ANOVA was performed to obtain p values, and Tukey’s multiple-comparison test was carried out to find statistical significance between groups. P = 0.0344; *, P < 0.05. (E) The checkpoints were induced in the same set of cells (i.e., those used as described in the panel C and D legends) after arresting them at G1, and Rad53 phosphorylation levels were detected. Actin was used as a loading control.