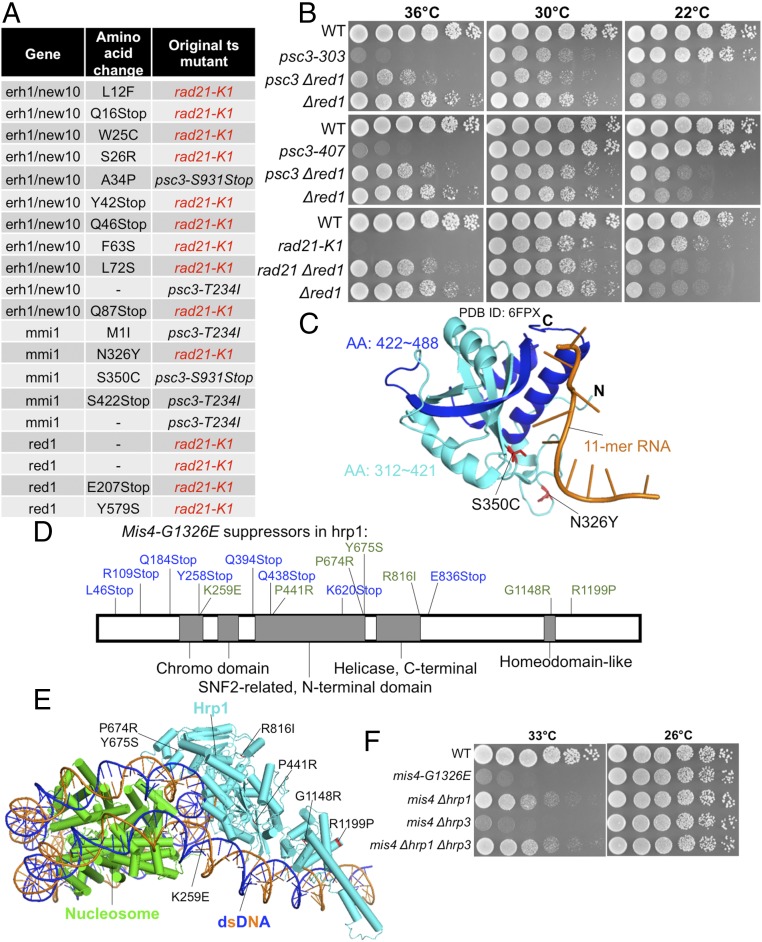
Fig. 3.
Suppressors of rad21-K1, psc3-T234I, and psc3-S931Stop reside in erh1/new10, mmi1, and red1 loci, all of which are involved in mRNA elimination. (A) Suppressors in erh1/new10, mmi1, and red1 that were obtained as spontaneous suppressors for ts rad21 and psc3. (B) Suppression of the ts phenotype of psc3 and rad21 by ∆red1 is shown. The ∆red1 is cs. WT, wild type. (C) Mmi1 mutations in an Mmi1 structure in complex with an 11-mer RNA (PDB ID code 6FPX) (Materials and Methods). Mmi1 contains a YTH domain at its C terminus that binds specific RNA sequences. Mmi1-S326 and Mmi1-S350 were located in Mmi1’s YTH domain. Mmi1-S326Y and Mmi1-S350C mutations may disrupt Mmi1’s ability to bind RNA directly. Mmi1-S422Stop causes loss of the Mmi1 C terminus (blue); therefore, it cannot bind RNA. AA, amino acid. (D) mis4-G1326E extragenic suppressors were mapped onto a chromosome remodeling factor gene, hrp1. (E) Hrp1 mutation in a nucleosome-Hrp1 structure (PDB ID code 5O9G) (Materials and Methods). (F) ∆hrp1 (but not another chromosome remodeling factor mutant, ∆hrp3) rescued mis4-G1326E at 33 °C too.