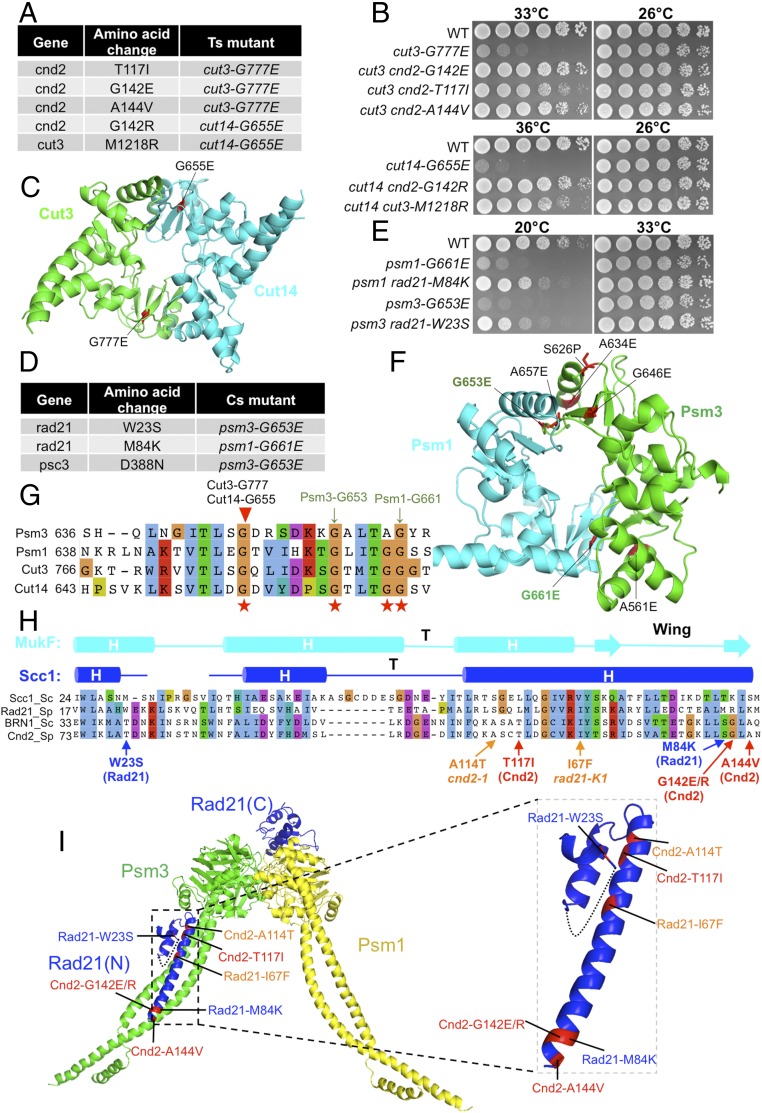
Fig. 4.
Suppressors of condensin hinge ts mutants and cohesin hinge cs mutants. (A) Suppressors in the cnd2 and cut3 head domain obtained from condensin hinge ts mutants (cut3-G777E and cut14-G655E). (B) Suppression of the condensin hinge ts mutants by the suppressors in A. WT, wild type. (C) Localization of Cut14-G655E and Cut3-G777E in the condensin hinge structure. Both mutations are located in hinge dimer interfaces. (D) Suppressors in rad21 and psc3 obtained from cohesin hinge cs mutants. (E) Suppression of cohesin hinge cs mutants by the suppressors in D. (F) Localization of Psm3-G653E and Psm1-G661E in the cohesin hinge structure. (G) Localization of the corresponding condensin hinge ts mutations in A and cohesin hinge cs mutations in D in a protein alignment of the hinges. (H) Localization of condensin hinge and cohesin hinge suppressors in a protein alignment of kleisin N termini. The secondary structure is predicted based on the structure of the S. cerevisiae Scc1 N terminus. Condensin hinge suppressors are shown in red, and cohesin hinge suppressors are shown in blue. In addition, responsible mutations of ts mutants cnd2-1 (A114T) and rad21-K1 (I67F) that are located in their N termini are shown (orange). (I) Localization of the mutations from H in the structure. All of them may directly affect kleisin’s interaction with the SMC head-coiled coil junction. Condensin hinge suppressors (Cnd2-T117I, Cnd2-G142E/R, and Cnd2-A144V) and cohesin hinge suppressors (Rad21-W23S and Rad21-M84K) may enhance kleisin’s interaction with the SMC head-coiled coil junction, while the cnd2-1 mutation A114T and rad21-K1 mutation I67F may disrupt this interaction.