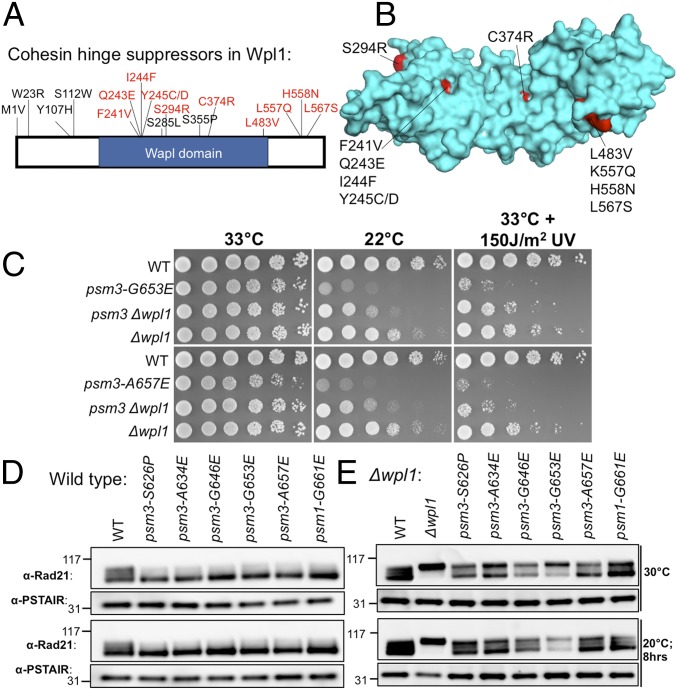
Fig. 5.
Suppression of cohesin hinge cs mutants by wpl1. (A) Localization of single amino acid substitutions in Wpl1 protein that rescued cohesin hinge cs mutants. Fifty-nine suppressors in wpl1 that suppressed cohesin hinge cs mutants were obtained, and some of them are nonsense mutations or indels. (B) Localization of the mutation sites on the Wpl1 structure (PDB ID code 3ZIK) (Materials and Methods). (C) Suppression of cohesin hinge cs mutants by ∆wpl1 (more spot results are shown in SI Appendix, Fig. S6A). These cohesin hinge cs mutants are hypersensitive to UV light. The UV sensitivity of these cs mutants was rescued by ∆wpl1 too (more spot results are shown in SI Appendix, Fig. S6A). WT, wild type. (D) Rad21 phosphorylation level in WT and cohesin hinge cs mutants detected using an anti-Rad21 polyclonal antibody (17, 64). Rad21 phosphorylation serves as an indicator of functional cohesin (8). (E) Rad21 phosphorylation level in WT, ∆wpl1, and hinge ∆wpl1 double mutants. Wpl1 and Pds5 bind the cohesin head and function as cohesin-releasing factors.