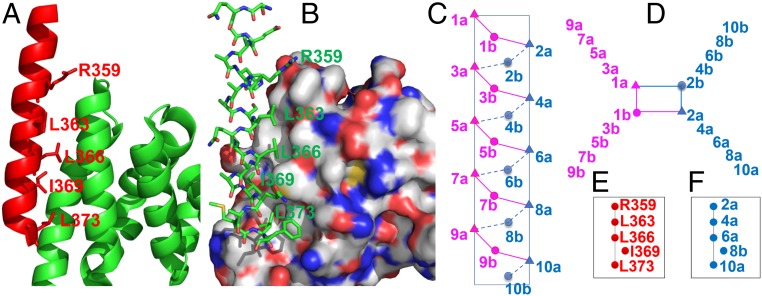
Fig. 2.
(A and B) The α-helical HD2 domain of BCL9, which directly engages a surface groove of β-catenin, provided the template for structural stabilization by hydrocarbon stapling [Protein Data Bank (PDB) ID code 2GL7]. (A) Cartoon representation of the residues of BCL9 (red) critical for binding to β-catenin, shown as sticks. (B) BCL9 shown as sticks, and β-catenin represented with the surface model. (C–F) Schematic representation of distribution of side chains from sulfono-γ-AApeptides. (C) Side view. (D) Top view, helical wheel. (E) Position map of critical residues of the BCL9 helix. (F) Position map of side chains of sulfono-γ-AApeptides designed to mimic residues in E.