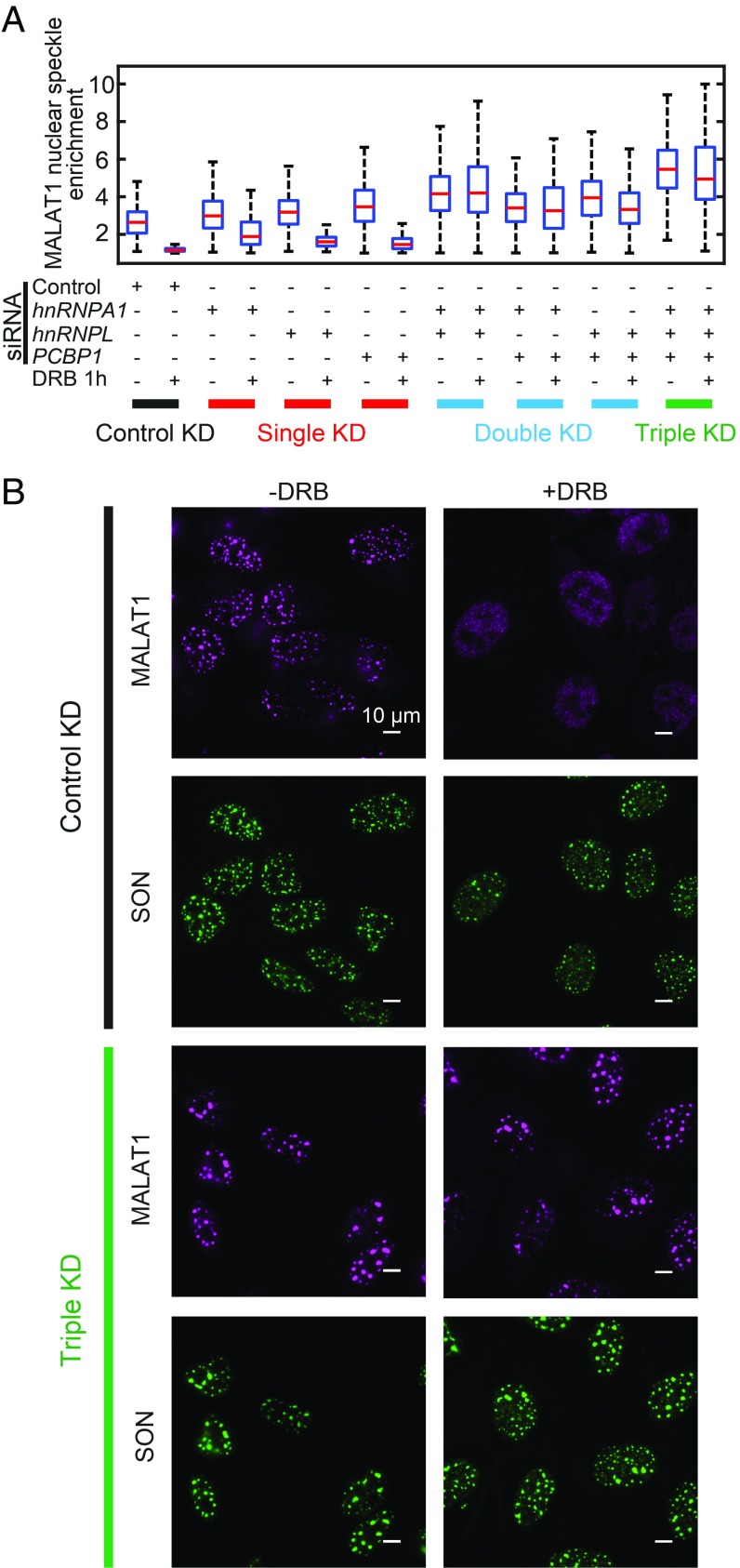
Fig. 6.
hnRNPA1, hnRNPL, and PCBP1 are required for transcription inhibition-induced dissociation of MALAT1 from nuclear speckles. (A) Quantifications of MALAT1 nuclear speckle enrichment with or without transcription inhibitor DRB treatment (50 µM for 1 h) for cells transfected by different combination of siRNAs. Between 100 and 300 cells are quantified for each condition. The transcription inhibition-induced dissociation of MALAT1 from nuclear speckles is not rescued by single knockdowns of hnRNPA1, hnRNPL, and PCBP1 but is rescued by the double-knockdown and triple-knockdown of these factors. (B) Images showing that in cells transfected by control siRNAs, MALAT1 dissociates from nuclear speckles on transcription inhibition; whereas in cells cotransfected by siRNAs targeting hnRNPA1, hnRNPL, and PCBP1, transcription inhibition fails to dissociate MALAT1 from nuclear speckles. The MALAT1 staining is shown in magenta, and SON staining is shown in green. (Scale bars: 10 µm.)