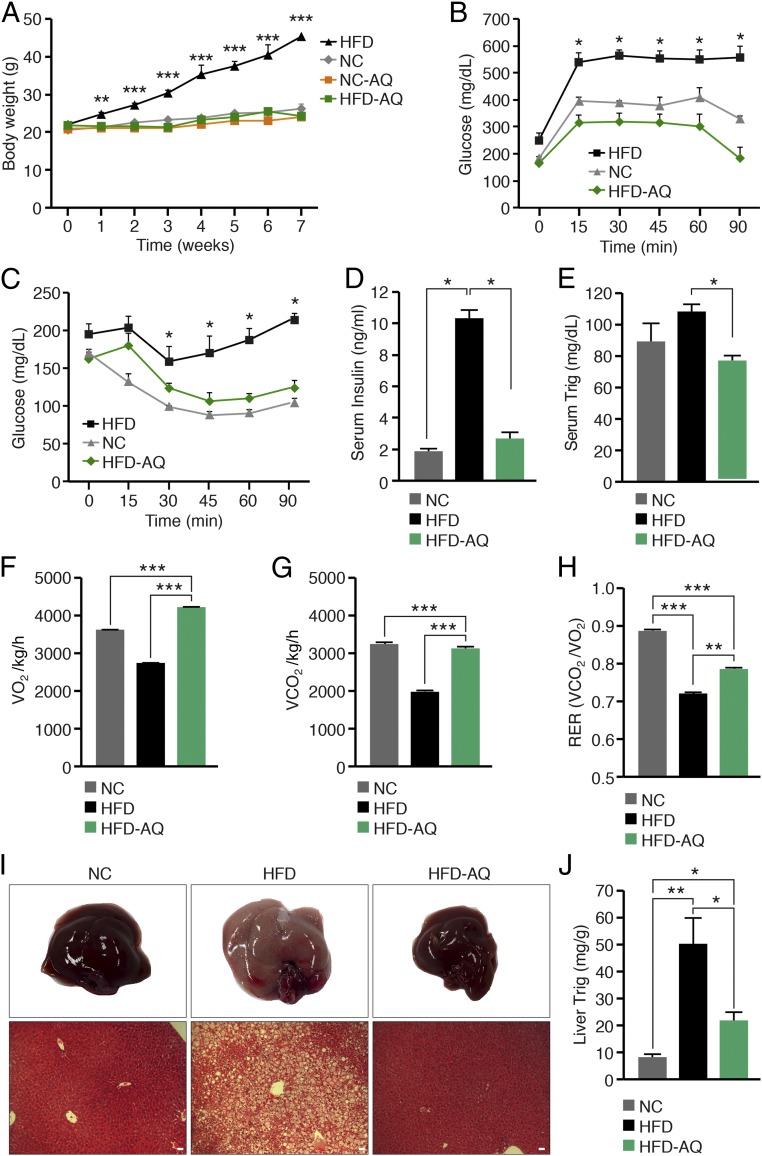
Fig. 5.
Putative NURR1 agonist AQ confers resistance to obesity and prevents HFD-induced hepatic steatosis. (A) Weekly body weight of mice on NC or HFD in the presence or absence of AQ. (B) Glucose tolerance of mice on NC or HFD in the presence or absence of AQ. Values were measured after 7 wk. (C) Insulin tolerance of mice on NC or HFD in the presence or absence of AQ. Values were measured after 8 wk. (D) Serum insulin levels in the postprandial state of mice on NC or HFD in the presence or absence of AQ. Values were measured after 10 wk. (E) Serum Trig levels in the postprandial state of mice on NC or HFD in the presence or absence of AQ. Values were measured after 10 wk. (F–H) Average oxygen consumption per h (F), carbon dioxide production during the light/dark cycle normalized to lean mass (G), and respiratory exchange ratio (H) of mice on NC or HFD in the presence or absence of AQ. Values were measured after 10 wk. (I) AQ prevents hepatic steatosis in WT mice on HFD. Livers were analyzed after 10 wk on NC or HFD in the presence or absence of AQ. (I, Lower) H&E staining. (Scale bars, 50 μm.) (J) Quantification of liver Trig levels of mice on NC or HFD in the presence or absence of AQ after 10 wk. Data are represented as mean ± SEM. n = 6 for HFD. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.005, ***P < 0.0005.