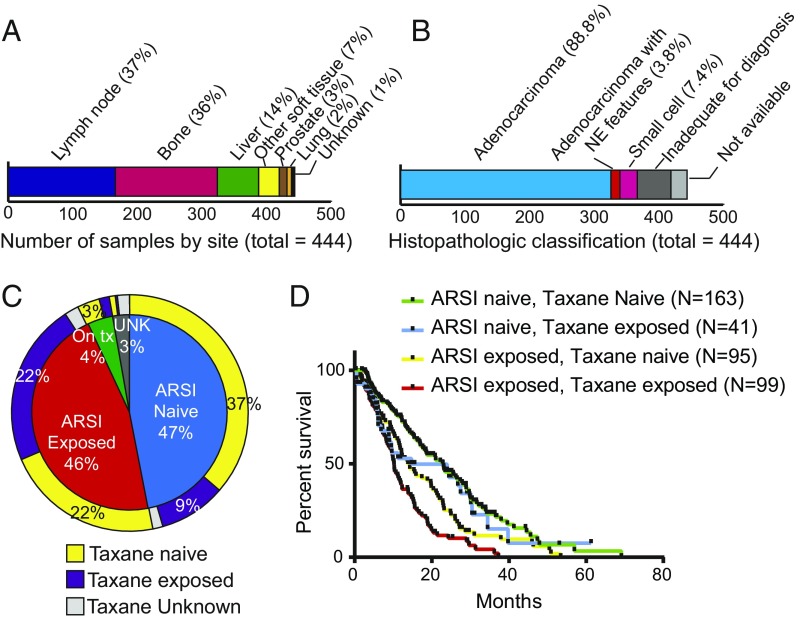
Fig. 1.
Overview of sample and patient characteristics for 444 tumors from 429 patients with mCRPC. (A) Site of mCRPC tumors profiled. (B) Histopathologic classification of profiled tumors. Tumors were classified by central review as adenocarcinoma, pure small-cell/neuroendocrine cancer, adenocarcinoma with neuroendocrine features (also included mixed acinar/neuroendocrine carcinoma), or could not be classified due to scant material or no tumor visible on the slides that were available for review despite successful sequencing. (C) Patient exposure status to next-generation AR signaling inhibitors (abiraterone acetate, enzalutamide, or ARN509) and to taxanes at the time of biopsy for the 444 profiled tumors. (D) Overall survival (OS) from the date of biopsy of the profiled tumor. OS was longer for tumors from ARSI- and taxane-naive patients compared with patients who had received an ARSI before the biopsy (P < 0.01, log-rank test). Survival was shortest when the patient had received both an ARSI and taxane chemotherapy at the time of biopsy.