FIGURE 5.
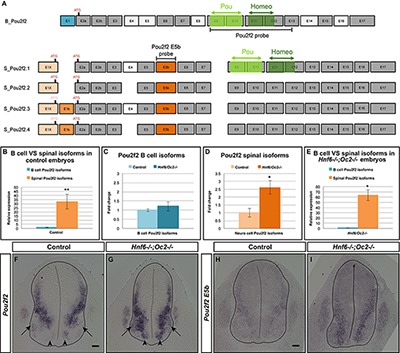
Onecut factors control expression of spinal cord-specific isoforms of Pou2f2. (A) The different Pou2f2 isoforms present in the B cells (B_Pou2f2) are characterized by invariant exons (dark gray) and alternative exons 4, 5, 8, 14, or 16 (light gray). They contain a POU-specific domain (light green) encoded by exons 9 and 10 and a POU-type homeodomain (dark green) encoded by exons 11 and 12. The four spinal Pou2f2 isoforms (S_Pou2f2.1–S_Pou2f2.4) (identified in the spinal cord) are characterized by a distinct exon 1 (E1X in light orange), an additional exon E5b (dark orange) and alternative exons E1b and 4 (medium orange and light gray, respectively). The presence of E1b disrupts the reading frame and imposes the use of the ATG located in E2a, whereas the absence of E1b leaves open the use of the ATG located in E1X. The regions corresponding to the generic or to the E5b in situ hybridization probes are indicated. (B–E) Quantification of spinal Pou2f2 or B-cell isoforms by RT-qPCR. (B) In control spinal cords, spinal Pou2f2 isoforms are >30-fold more abundant than B-cell isoforms. (C) B cell Pou2f2 isoforms barely trend to increase in the absence of OC factors. (D) In contrast, spinal Pou2f2 isoforms are 2.6-fold overexpressed in Hnf6-/-;Oc2-/- spinal cords. (E) In double mutant spinal cords, spinal Pou2f2 isoforms are >60-fold more abundant than B-cell isoforms. (F–I) In situ hybridization labelings on transverse sections (brachial level) of control or Hnf6-/-;Oc2-/- spinal cords at e11.5 with (F,G) a generic Pou2f2 probe complementary to spinal and to B-cell isoforms (A) or (H,I) a spinal isoform-specific probe corresponding only to exon E5b (A). (F,H) In control embryos, Pou2f2 is strongly expressed in ventral and in dorsal interneuron populations, and more weakly in the ventral motor neuron area. (G,I) In OC mutant embryos, Pou2f2 is upregulated in interneuron populations and its expression is expanded in ventral populations (arrowheads) and in the motor neurons (arrows). ∗p ≤ 0.05; ∗∗p ≤ 0.01. Scale bars = 50 μm.
