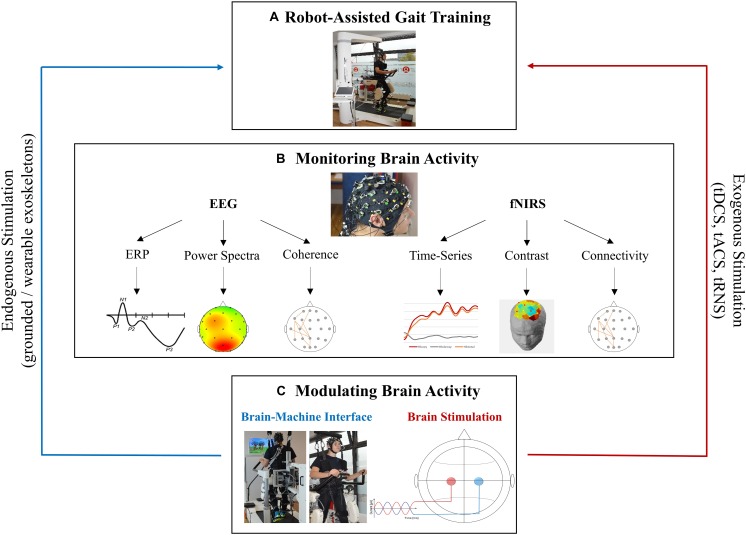
FIGURE 2.
Future perspectives for fused EEG-fNIRS in robotic gait rehabilitation. (A) Robotic device Lokomat (Hocoma, Switzerland) for RAGT. (B) EEG and fNIRS provide the monitoring of neurophysiological processes occurring during RAGT by measuring different perspectives of brain activity. Electrophysiological (EEG) and haemodynamic (fNIRS) signals can be processed in various ways. Data from each electrode/channel can be extracted over time (e.g., ERPs/time-series), as an average over time (e.g., power spectra/contrasts) or they can be correlated to represent functional connectivity (e.g., coherence/connectivity). (C) Brain activity measured by EEG or fNIRS serves as a basis for brain modulation such as BCI/BMI which may be a form of endogenous brain stimulation as well as for brain stimulation techniques were a weak current is applied through the skull to modulate brain activity. Subjects appearing in the figures provided informed written consent to the publication of identifying images in an online open access publication.