Figure 4. Scales vascularize independently of sensory axons:
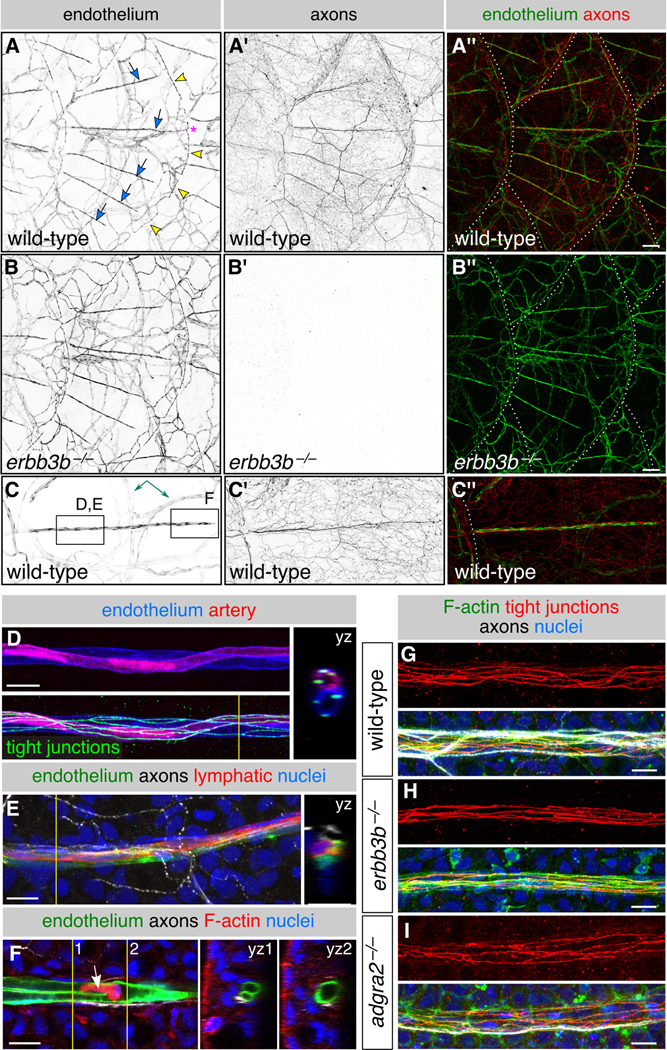
(A-C) Representative lateral views of the trunk from wild-type and erbb3b−/− adults. Arrows, superficial scale capillaries. Arrowheads, microvasculature associated with scale margin. Asterisk, interconnection of superficial capillary with scale margin vasculature. Dashed lines, scale margins. Double-headed arrow, example of dermal vasculature not associated with sensory nerves. Boxes in C indicate areas of magnification for panels D-F. (D,E) Magnification of scale capillaries. Note the two intertwined vessels in panel D. (F) Single z-section through the tip of a scale capillary. Orthogonal views show that vessel lumens merge near posterior tip to form a U-shape. Arrow, cell within the vessel lumen. Yellow lines in D-F, planes of orthogonal sections. (G-I) Representative scale capillaries immunostained for the indicated markers from adult wild-type, erbb3b−/− and adgra2−/− fish. Transgenes: endothelium [Tg(fli1a:EGFP)]; (A-C) axons [Tg(p2rx3a>mCherry)]; (D) artery [Tg(−0.8flt1:RFP)] (Bussmann et al., 2010) lymphatic [TgBAC(prox1a:KALTA4,4xUAS-ADV.E1b:TagRFP)] (van Impel et al., 2014). Staining: (D) tight junctions (anti-Tjp1); (E) axons (acTubulin) and nuclei (DAPI); (F) F-actin (phalloidin), axons (acTubulin) and nuclei (DAPI); (G-I) F-actin (phalloidin), tight junctions (anti-Tjp1), axons (acTubulin) and nuclei (DAPI). Scale bars, 100 μm (A-C) and 10 μm (D-I). See also Figure S4.
