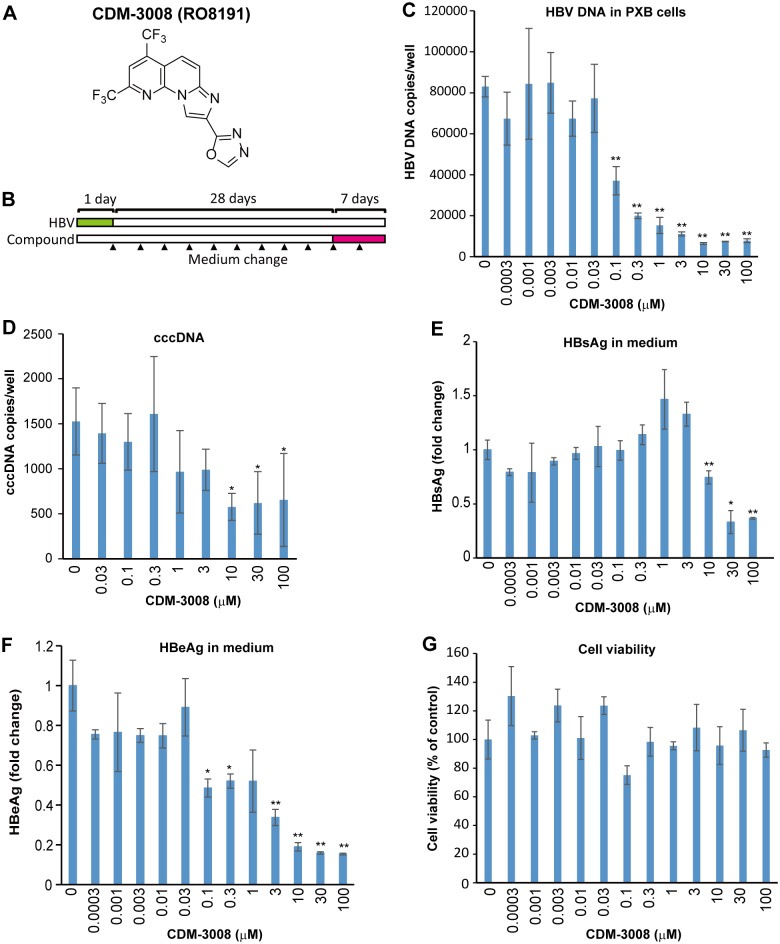
Fig 1. Anti-HBV activity of CDM-3008 in primary cultured human hepatocytes.
(A) The chemical structure of CDM-3008. (B) The schematic experimental design of the anti-HBV activity analysis. Primary cultured human hepatocytes (PXB cells) were infected with HBV genotype C for 1day (green) and cultured for 28 days, and the cells were then treated with 0–100 μM CDM-3008 for 7 days (magenta). The black triangles show the time points of medium changes. (C) Measurement of HBV DNA copies in PXB cells after 7 days of CDM-3008 treatment. HBV DNA was decreased with 0.1–100 μM CDM-3008 in a dose-dependent manner. (D) Measurement of cccDNA copies after T5 exonuclease treatment. cccDNA was significantly decreased with 10–100 μM CDM-3008. Error bars indicate S.D. in D (n = 3). *, p < 0.05 (one-tailed t-test) in D. (E) HBsAg levels are shown as fold changes. HBsAg levels were significantly decrease with 10–100 μM CDM-3008. (F) HBeAg levels are shown as fold changes. HBeAg levels were significantly decreased with 0.1–100 μM CDM-3008. (G) Cell viabilities were shown as % of control DMSO. Error bars indicate S.D. in C, E-G (n = 3). *, p < 0.05 and **, p < 0.01 (two-tailed t-test) in C, E-G.