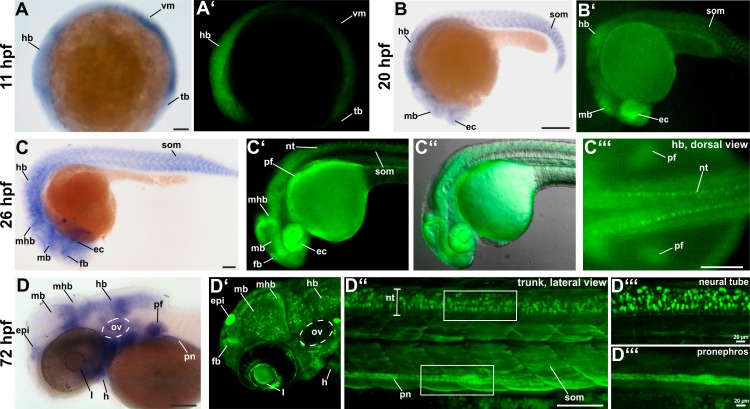
Fig 1. Comparison between endogenous tcf12 mRNA expression detected by whole mount in-situ hybridization and EGFP expression in Tg(-2.1tcf12:EGFP) fish.
(A, A’) tcf12 transcripts are detectable by whole mount in-situ RNA hybridization at 11 hpf onwards in the hindbrain, ventral mesoderm, and tailbud. The expression pattern equals the first detectable EGFP signal in Tg(-2.1tcf12:EGFP) zebrafish. (B, B’) In-situ hybridization and transgenic embryos demonstrate tcf12 expression in the eyecups, midbrain, hindbrain, and somites at 20 hpf. (C) 26 hpf old zebrafish embryos show an additional tcf12 expression domain in the forebrain and the midbrain-hindbrain boundary. (C’, C”, C”‘) EGFP is also detected in the pectoral fin buds and in the neural tube of transgenic fish. (D, D’, D”; D”‘) In 72 hpf old fish tcf12 expression can, in addition, be detected in the epiphysis, the otic vesicle, the pronephros, and the heart. Images in D”‘ show magnifications of the neural tube and pronephros shown in D”. ec, eye cups; epi, epiphysis; fb, forebrain; h, heart; hb, hindbrain; hpf, hours post fertilization; l, lens; mb, midbrain; mhb, midbrain-hindbrain boundary; nt, neural tube; ov, otic vesicle; pf, pectoral fins; pn, pronephros; som, somites; tb, tailbud; vm, ventral mesoderm. All scale bars represent 100 μm unless otherwise stated.