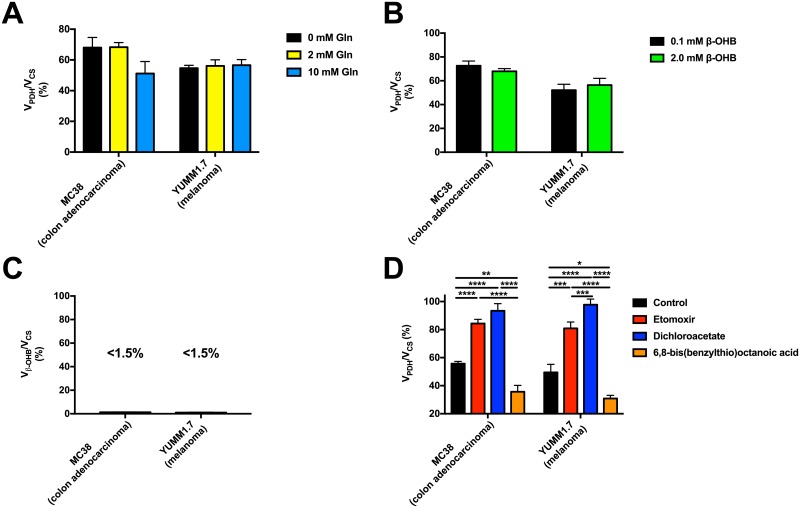
Fig 3. The stable isotope method applied in this study is sensitive to detect the expected differences in VPDH/VCS with physiologic alterations in these fluxes, and is not affected by physiologically relevant glutamine or ketone concentrations.
(A) Glutamine in the physiologic range (0–10 mM) does not significantly affect the measured VPDH/VCS in MC38 or YUMM1.7 cells. n = 4 replicates per condition, with comparisons by ANOVA with Bonferroni’s multiple comparisons test. (B) β-OHB in the physiologic range (0–2 mM) does not significantly alter the measured VPDH/VCS in MC38 or YUMM1.7 cells. Conditions were compared by the 2-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test. In panels (B)-(D), n = 6–9 replicates per condition. (C) Vβ-OHB-ox/VCS is minimal in MC38 and YUMM1.7 cells. (D) VPDH/VCS is increased with inhibition of fatty acid oxidation (etomoxir) or stimulation of PDH (dichloroacetate), and decreased with inhibition of PDH (6,8-bis(benzylthio)octanoic acid). Groups were compared by ANOVA with Bonferroni’s multiple comparisons test. In all panels, data are the mean ± S.E.M.