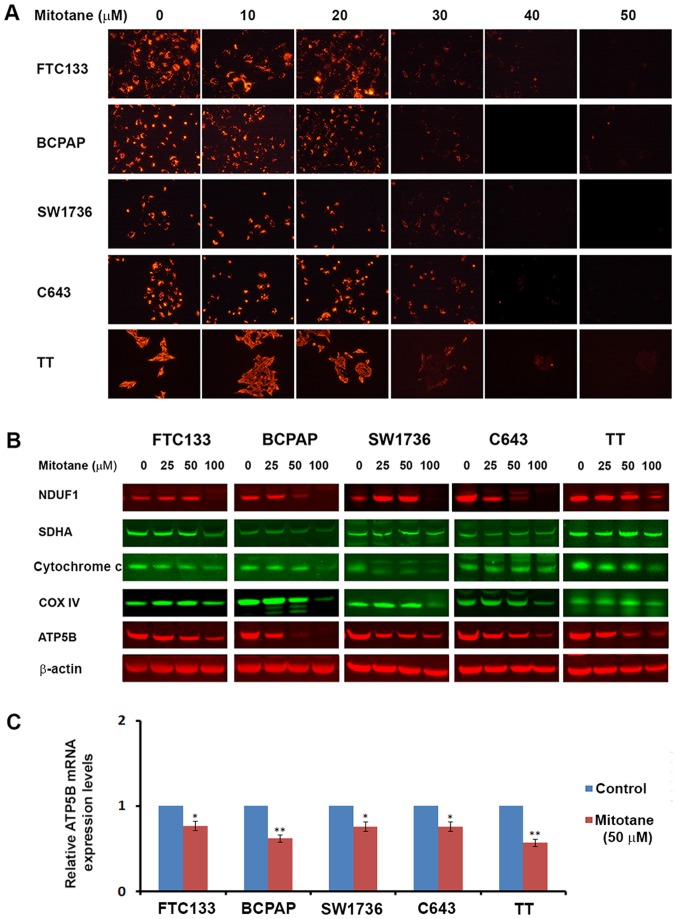
Figure 3.
Mitotane affects mitochondrial activity in thyroid cancer cell lines. (A) Thyroid cancer cells were treated with increasing concentrations of mitotane (0-50 μM) and stained with JC-1. Treatment with mitotane was associated with a dose-dependent decrease of fluorescence, indicating progressive loss of mitochondrial activity. Treatment with 30 μM mitotane resulted in inhibition of mitochondrial membrane potential in all examined thyroid cancer cell lines. (B) Detection of mitochondrial proteins NDUFA1 (complex 1), SDHA (complex 2), cytochrome c, COX4 (complex 4) and ATP5B (complex 5) in thyroid cancer cell lines following 24-48-h treatment with 0-100 μM mitotane by western blot analysis. Treatment led to a decrease in the levels of proteins regulating oxidative respiration in a dose-dependent and cell type-specific manner. (C) The effects of mitotane on ATP5B mRNA levels in thyroid cancer cells. The relative mRNA levels of ATP5B were evaluated following normalization to 18S RNA levels. Thyroid cancer cell treatment with 50 μM mitotane for 24 h resulted in downregulation of ATP5B expression, with the most marked effects observed in the medullary thyroid cancer-derived TT cells. Relative expression is presented normalized to the untreated control. *P<0.05 and **P<0.01 versus untreated control. The data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation. NDUFA1, NADH dehydrogenase 1 α-1; SDHA, succinate dehydrogenase flavoprotein subunit; COX4, cytochrome c oxidase subunit 4; ATP5B, ATP synthase subunit β.