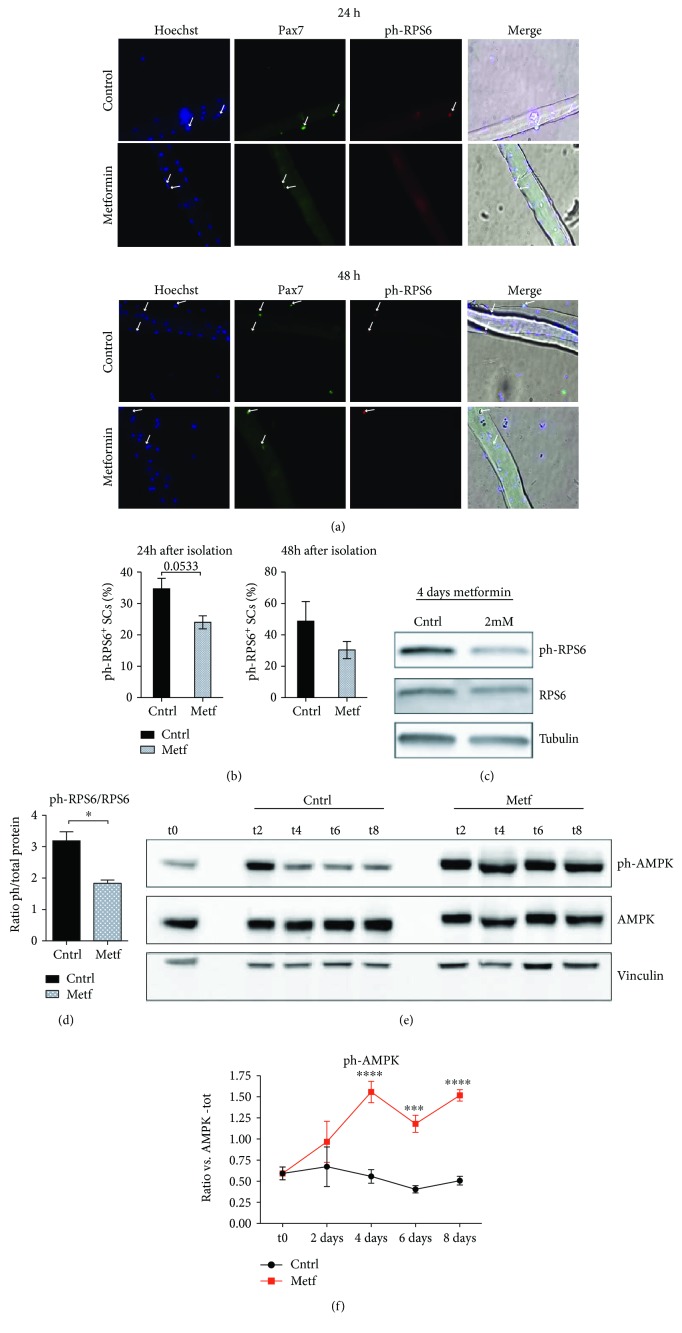
Figure 5.
Metformin negatively modulates the phosphorylation of RPS6 in SCs. (a) Single myofibers were isolated from C57BL/6 mice and treated in vitro with 2 mM metformin. The SCs associated with the myofibers were analyzed by immunofluorescence microscopy for the expression of Pax7 and p-RPS6 after 24 h and 48 h of culture. (b) The percentage of SCs that are positive for p-RPS6 after 24 h and 48 h in culture was calculated after three independent single-fiber isolations and experimental replicates. Statistical significance was evaluated by Student's t-test (∗ p < 0.05) (number of counted SCs in each sample: 24 h control = 86, 24 h metf = 82, 48 h control = 72, and 48 h metf = 69). (c) Isolated SCs were treated in vitro for 4 days with 2 mM metformin, and protein extracts were analyzed by SDS-PAGE for the expression of ph-RPS6 and total RPS6 protein. Tubulin was used as a loading control. (d) Quantitation graph of ph-RPS6 to total RPS6 protein levels monitored by western blot in three independent cell isolations and biological replicates (n = 3). Statistical significance was evaluated by Student's t-test (∗ p < 0.05). (e) Western blot analysis for the expression of ph-AMPK and total AMPK protein of control and metformin-treated SCs after 2, 4, 6, and 8 days of treatment (t2, t4, t6, and t8, respectively). Vinculin was used as a loading control. (f) Quantitation graph of ratio ph-AMPK/total AMPK monitored by western blot in four independent cell isolations and biological replicates (n = 4). Statistical significance was evaluated by the ANOVA test (∗∗∗∗ p < 0.0001).