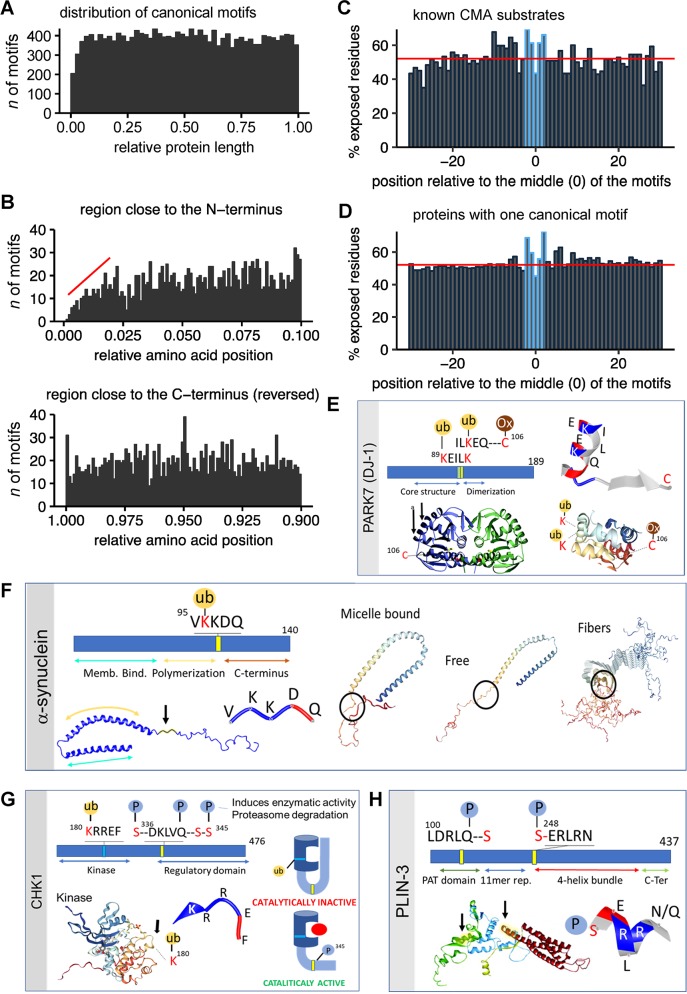
Fig 2. Distribution of KFERQ-like motifs within protein sequences.
(A) Distribution of canonical KFERQ-like motifs along the protein length (normalized to a scale from 0 [N-terminus] to 1 [C-terminus]). The histograms show the count of motifs at the relative position with a bin size of 0.02. (B) The first 10% (N-terminus; top) and last 10% (C-terminus; bottom) of the normalized protein length in Fig 2A, shown here with a bin size of 0.001. The C-terminal plot (bottom) is mirrored for easier comparison. The red line indicates the slope of the reduction in KFERQ-like motifs. (C, D) Bar plots showing the average of exposed amino acids, as predicted from the primary sequence, using JPred4 for proteins validated as CMA substrates (C) or proteins in the human proteome harboring one canonical motif (D). For each protein, a region ±30 amino acids around the central amino acid of the motifs was isolated and aligned on the KFERQ-like motifs. The percentage of exposed residues was then calculated for each position. The red line indicates the mean percentage of exposure for all amino acids in all investigated proteins. Amino acids that are part of the KFERQ-like motifs are highlighted in blue. (E-H) Examples of domain localization and experimentally confirmed PTMs in KFERQ-like motifs of DJ-1 (E), alpha-synuclein (F), CHK1 (G) and PLIN3 (H). Canonical motifs are marked as yellow bars, phosphorylation-generated in blue, and acetylation-generated in green. Protein structures were obtained from the RCSBPDB protein data bank (rcsb.org) using PBD IDs 1j42 (for DJ-1 [25]); 1XQ8, 2KKW, and 2N0A (for alpha-synuclein [26]); 4FSM (for Chk1 [27]); and 1SZI (for PLIN3 [28]). The structures of the KFERQ-like motifs are shown as strings and ribbons colored based on amino acid properties. PTMs shown: ubiquitylation (ub), phosphorylation (P), and oxidation (Ox). Arrows: location of the motif in the protein structure. The cartoon in (G) depicts the conformational change in Chk1 that releases autoinhibition of its catalytic activity. CHK1, checkpoint kinase 1; CMA, chaperone-mediated autophagy; Memb. Bind., Membrane Binding; Ox, oxidation; P, phosphorylation; PARK7, Parkinsonism associated deglycase; PAT, perilipin/ADRP/TIP47; PLIN3, perilipin 3; PTM, posttranslational modification; ub, ubiquitylation.