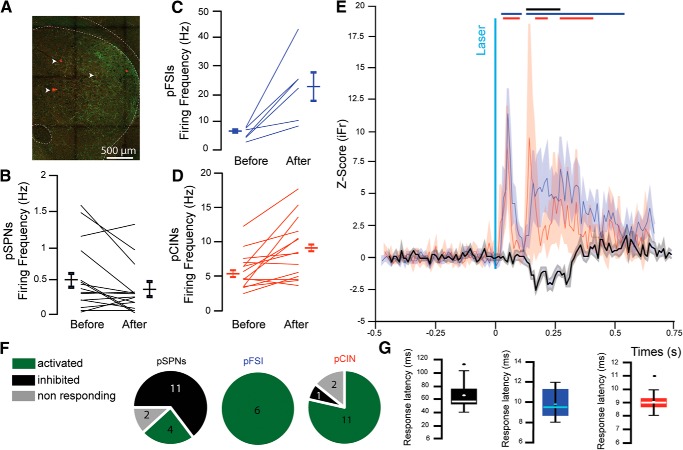
Figure 6.
Stimulation of PPN glutamatergic axons in the striatum in vivo activates interneurons and induces feedforward inhibition of pSPNs. A, Fluorescent image showing YFP-positive PPN axons (green) in the striatum in close proximity to the recording electrode tracks (white arrows). B–G, Changes in firing rate of pSPNs (B), pFSIs (C), and pCINs (D) before and after stimulation. E, Normalized z score of pSPNs (black), pFSI (blue), and pCINs (red) before and after stimulation. Bars indicate ±2 SD of the z score for each group. F, Proportion of responding neurons (≥2 SD from z score) identified as pSPN (left), pFSI (middle), or pCINs (right) following stimulation of PPN axons. G, Response latencies for pSPN (left, black), pFSI (middle, blue), or pCINs (right, red).