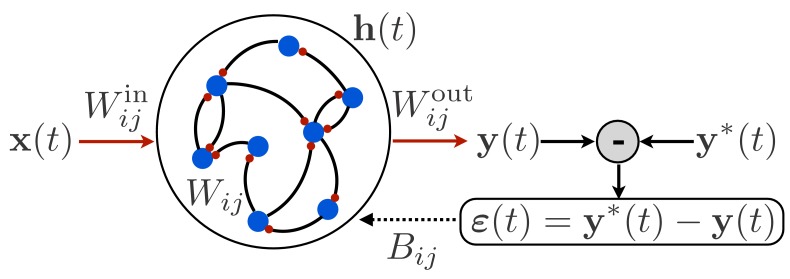
Figure 1. Schematic illustration of a recurrent neural network.
The network receives time-dependent input , and its synaptic weights are trained so that the output matches a target function . The projection of the error with feedback weights is used for learning the input weights and recurrent weights.