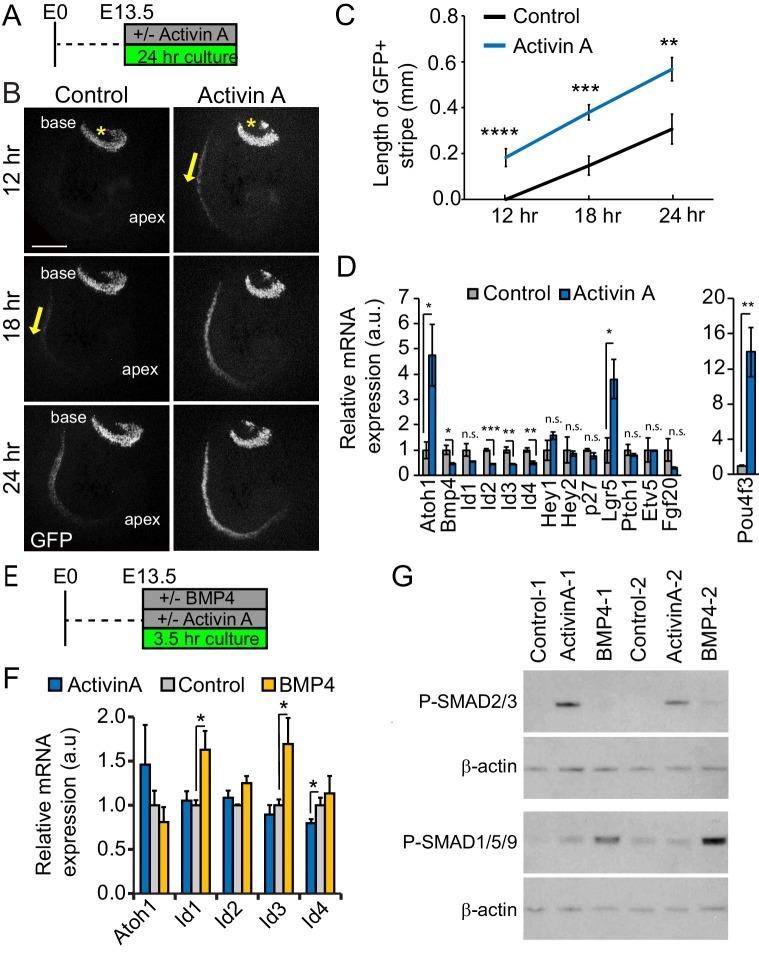
Figure 2. Activin A promotes auditory hair cell differentiation.
(A) Experimental design for B-D. Stage E13.5 wild type cochlear explants were cultured with or without Activin A (final conc. 500 ng/ml) for 24 hr. (B) Atoh1-GFP reporter expression (GFP, gray) was used to monitor and analyze hair cell differentiation in Activin A-treated and control cochlear explants. Asterisks mark the vestibular saccule that contain GFP positive hair cells. Yellow arrows mark the onset of hair cell differentiation within the cochlea. Scale bar, 100 µm. (C) Quantification of basal-to-apical extent of hair cell differentiation in control versus Activin A-treated cochlear cultures (B). Data expressed as mean ± SEM (n = 5–8 cochlear explants per group, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001, student’s t-test). (D) Transcript levels of pro-sensory genes (Id1-4, Hey1, Hey2, p27, Etv5, Fgf20, Ptch1) and hair cell-specific genes (Atoh1, Pou4f3) were analyzed in enzymatically purified cochlear epithelia. Data are mean ± SEM (n = 3 biological replicates, *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, student’s t-test). (E) Experimental design for F, G. Stage E13.5 wild type cochlear epithelia were cultured with or without Activin A (final conc. 200 ng/ml) or BMP4 (final conc. 100 ng/ml) for 3.5 hr. (F) RT-qPCR analysis reveals differential response to Activin A and BMP4 treatment. Individual cochlear epithelia were analyzed. Data are mean ± SEM, n = 4 biological replicates, *p<0.05. (G) Activin A induces SMAD2/3 phosphorylation in cochlear epithelial cells. Western blot analysis was used to detect phosphorylated (p) SMAD2/3 and p-SMAD1/5/9 proteins in individual cochlear epithelia after 3.5 hr culture with or without Activin A or BMP4. Beta-actin was used as loading control.