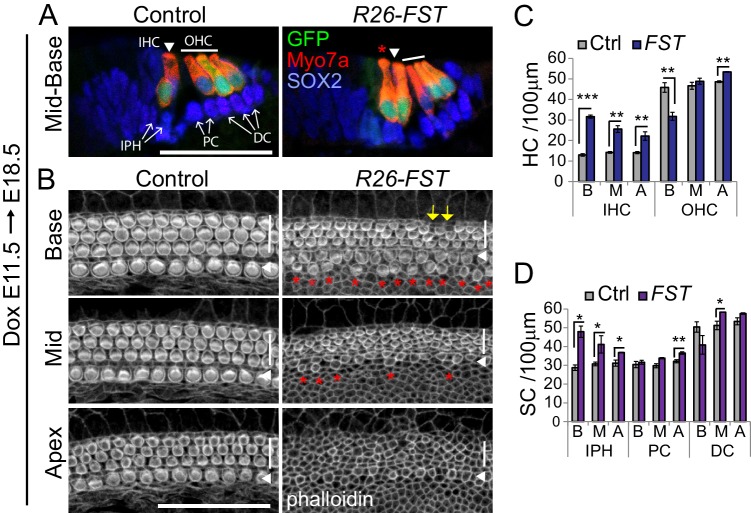
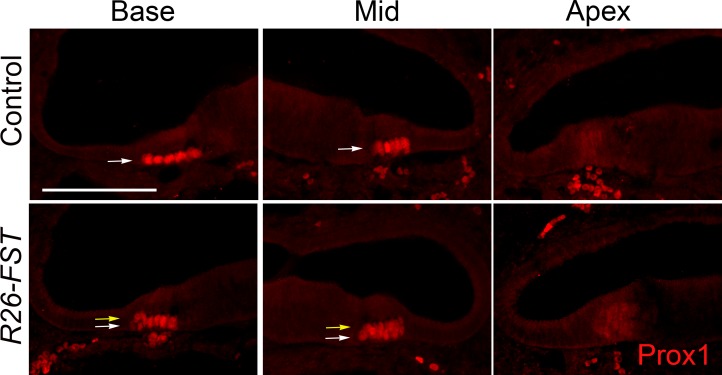
Figure 5. FST overexpression in the developing cochlea disrupts inner hair cell patterning and delays hair cell maturation.
FST transgenic (R26-FST) embryos and their control (wild type or single transgenic) littermates were exposed to dox starting at E11.5 until tissue harvest at E18.5. (A) FST overexpression results in ectopic inner hair cells. Shown are cross-sections through the cochlear mid-base of control and R26-FST transgenic embryos. GFP (green) and Myo7a (red) label inner hair cells (IHC, white arrowhead) and outer hair cells (OHC, white bar). Red asterisks mark ectopic inner hair cells. SOX2 (blue) labels supporting cells including inner phalangeal cells (IPH), pillar cells (PC) and Deiters’ cells (DC) indicated by white arrows. Scale bar 50 µm. (B) FST overexpression delays stereocilia formation. Shown are z-stack projections of the luminal surface of control and R26-FST transgenic cochlear sensory epithelia. Phalloidin labels actin-rich stereocilia of inner (white arrowhead) and outer hair cells (white bar). Red asterisks mark ectopic inner hair cells. Yellow arrows mark the location of missing outer hair cells. Scale bar 50 µm. (C–D) Quantification of hair cell (C) and supporting cell (D) density in the base, mid and apex of control (Ctrl, gray bars) and FST overexpressing (FST, purple bars) cochleae. Abbreviations: IHC, inner hair cells; OHC, outer hair cells; IPH, inner phalangeal cells; PC, pillar cells; DC, Deiters’ cells; B, base; M, mid; A, apex. Data expressed as mean ± SEM (n = 3 animals per group, *p≤0.05, **p<0.01, student’s t-test).