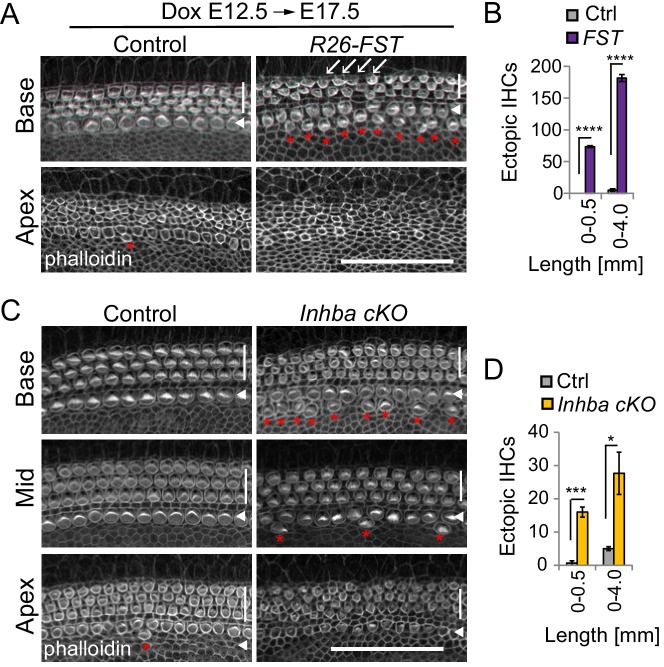
Figure 6. Activin signaling is required for patterning and maturation of hair cells.
(A–B) FST overexpression at E12.5 delays hair cell maturation and causes a mild overproduction of inner hair cells. FST transgenic (R26-FST) embryos and their control (single transgenic) littermates were exposed to dox starting at E12.5 until tissue harvest at E17.5. (A) Shown are the apical surfaces of hair cells located in the base, mid and apex of control and R26-FST transgenic cochlear sensory epithelia. Phalloidin labels actin-rich stereocilia of inner (white arrowhead) and outer hair cells (white bar). Red asterisks mark ectopic inner hair cells. White arrows mark location of missing outer hair cells. Scale bar 50 µm. (B) Graphed are the number of ectopic inner hair cells (IHC) within the most basal segment (0–0.5 mm) and within the entire length (0–4 mm) of control (Ctrl, gray) and FST overexpressing (FST, purple) cochleae. Data expressed as mean ± SEM (n = 3 animals per group, ****p<0.0001, student’s t-test). (C-D) Conditional ablation of the Inhba gene delays hair cell maturation and causes a mild overproduction of inner hair cells. (C) Shown are the apical surfaces of hair cells located in the base, mid and apex of stage P0 Inhba fl/fl (control) and Pax2-Cre Inhba fl/fl (Inhba cKO) cochlear sensory epithelia. Phalloidin labels actin-rich stereocilia of inner (white arrowhead) and outer hair cells (white bar). Red asterisks mark ectopic inner hair cells. Scale bar 50 µm. (D) Graphed are the number of ectopic inner hair cells (IHC) within the most basal segment (0–0.5 mm) and within the entire length (0–4 mm) of control (Ctrl, gray) and Inhba mutant (Inhba cKO, orange) cochleae. Data expressed as mean ± SEM (n = 3 animals per group, *p≤0.05, ***p<0.001).