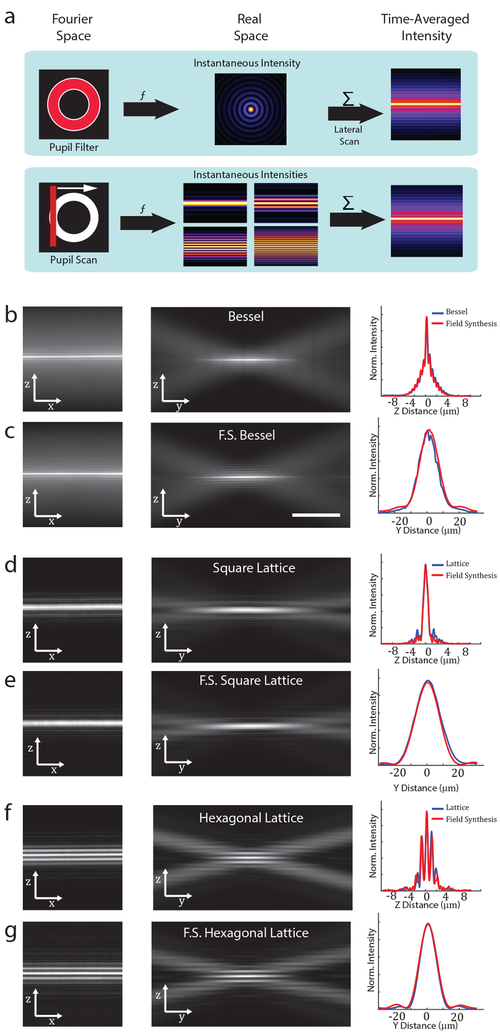
Figure 1.
Light-sheet generation by field synthesis. A, Top. In light-sheet microscopy, a pupil filter conjugate to the back-pupil plane of the illumination objective is used to shape the instantaneous laser focus at the front focal plane of the same objective. To generate a time-averaged sheet of light, the laser focus is rapidly scanned laterally. A, Bottom. Principle of field synthesis: a focused line is laterally scanned over a pupil filter, creating a time-averaged sheet of light in the front focal plane of the illumination objective. B, D, and F. Experimental examples of a Bessel beam light-sheet, square lattice, and hexagonal lattice, generated by traditional methods, respectively. C, E, and G. Experimental examples of a Bessel beam light-sheet, square lattice, and hexagonal lattice generated with Field Synthesis, respectively. The cross-sectional profiles are averaged over six spatial regions in each image dataset.