Fig. 9. SubP-induced frequency plasticity in pontine brainstem-spinal cords is abolished by a neurokinin-1 (NK1) receptor antagonist drug (L760735, 10 μM).
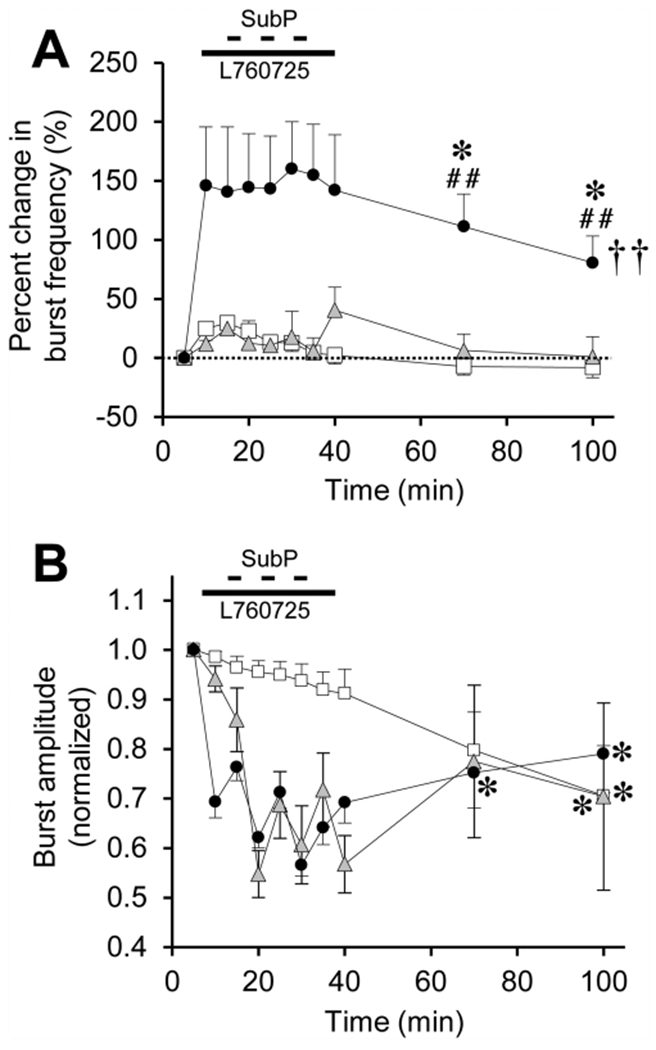
(A) The time course of burst frequency effects are shown for intermittent SubP applications alone (3-min application/7-min washout, ×3) at 100 nM (black circles; same data as in Fig. 5A), and intermittent SubP applications with L760735 pretreatment (gray triangles). Data from time control experiments are shown (white squares; same data as in Fig. 5A). No frequency plasticity was observed with L760735 treatment. (B) L760735 did not block the acute SubP-induced decrease in burst amplitude, and did not alter burst amplitude with respect to intermittent SubP applications only, or time control experiments. Statistics symbols as in Fig. 2 legend.
