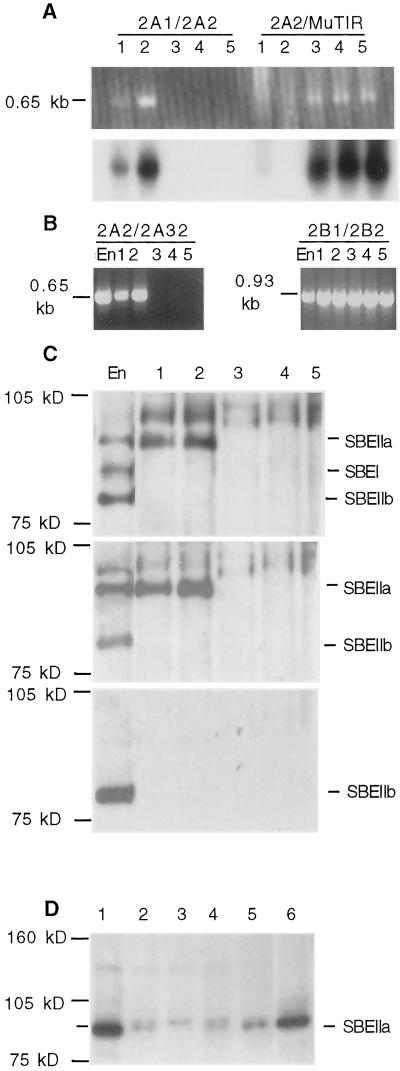
Figure 4.
Molecular analysis of sbe2a::Mu mutants. A through C, Selection of homozygous sbe2a::Mu mutants (lanes 3–5) and wild-type controls (lanes 1 and 2) and the expression patterns of SBEs as compared with inbred line W64A 20 DAP endosperm (En). D, Western analysis of mutant and control genotypes in kernels. A, Identification of sbe2a::Mu mutants and their full-sibling wild-type controls from a BC1F2 population. PCR was used to detect the wild-type allele (primers 2A1/2A2) and the mutant allele (primers 2A2/MuTIR) using DNA extracted from seedlings. Gel electrophoresis of PCR products (top) and hybridization to Sbe2a cDNA clone (bottom). B, RT-PCR analysis of homozygous sbe2a::Mu mutants and their full-sibling wild-type controls to detect transcripts in 30 DAE leaf tissue using primers 2A2 and 2A32 and Sbe2b primers 2B1 and 2B2. C, Western analysis of homozygous sbe2a::Mu mutants and their full-sibling wild-type controls to detect the presence of SBEI, SBEIIa, and SBEIIb in 30 DAE leaf tissue using the non-specific SBEI antibody (top). The high Mr proteins cross-reacting with this antibody are unknown. Identity of SBEIIa and SBEIIb were verified using antibodies to SBEIIa (middle) and SBEIIb (bottom). D, Western analysis of homozygous sbe2a::Mu mutants and controls to detect the presence of SBEIIa in dry kernel tissue using the SBEIIa antibody. Endosperm protein extracts are from fresh sweet corn (lane 1) and from dry kernels of an unrelated Mu mutant wild type for Sbe2a (lane 2), sbe2a:Mu(lane 3), ae-ref (lane 4), and W64A wild type (lane 5). Lane 6 contains protein extract from leaves of an sbe2a::Mu/Sbe2a heterozygote.