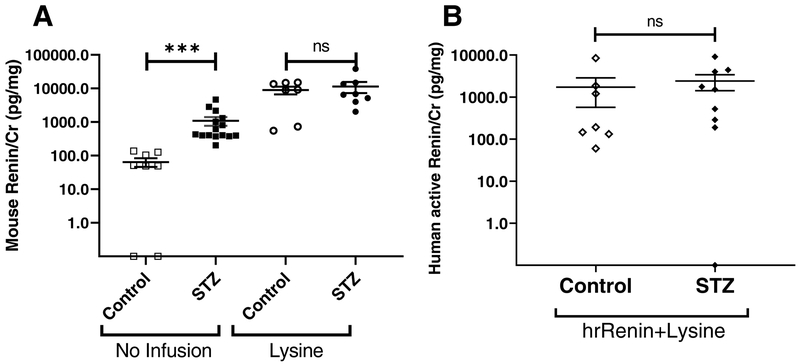
Figure 3. (A) Effect of lysine on urinary mouse renin in control and diabetic mice (B) Human active renin/Cr in non-diabetic and diabetic mice infused with human recombinant renin and lysine.
A: Mouse renin/Cr ratio in urines from control (white) and diabetic (black). Mice were infused with lysine [Lysine (circles); control n=7, diabetic n=8] or did not receive lysine infusion [no infusion (squares); control n=8, diabetic n=15]. In non-infused animals total renin was higher in STZ-treated compared to controls, whereas after lysine infusion no significant differences existed between the two groups. Data shown as mean ± SE. ***p<0.001.
B: In mice infused with both hrRenin and lysine, urinary human active renin/Cr is markedly elevated, but there is no significant difference in STZ treated (closed symbols) vs. non-diabetic mice (Control, open symbols). Human active renin is undetectable in urines from mice infused with lysine only or from mice not infused with hrRenin (not shown, see text). hrRenin: human recombinant renin; Data shown as mean ± SE