Figure 1.
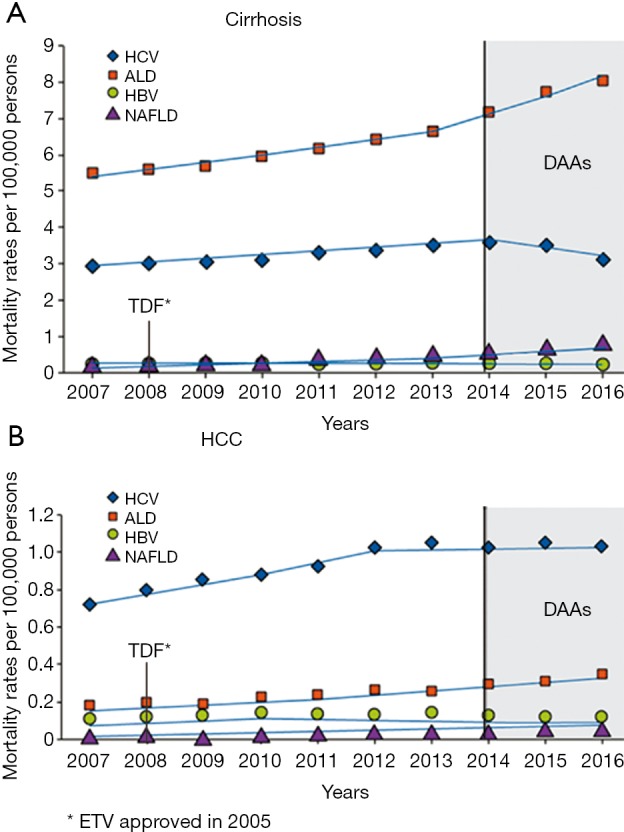
Age-standardized mortality rates for cirrhosis (A) and HCC (B) in United States between 2007 and 2016. HCV-related cirrhosis mortality significantly decreased after the introduction of DAAs while HCV-related HCC mortality did not increase. After the introduction of entecavir and tenofovir, mortality of HBV-cirrhosis significantly decreased and HBV-HCC mortality showed a decline trend. ALD and NAFLD mortality rates dramatically raised over the study period. Adapted from Kim et al. (9). ALD, alcoholic liver disease; DAA, direct antiviral agent; ETV, entecavir; HBV, hepatitis B virus; HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; HCV, hepatitis C virus; NAFLD, non-alcoholic liver disease, TDF, tenofovir.
