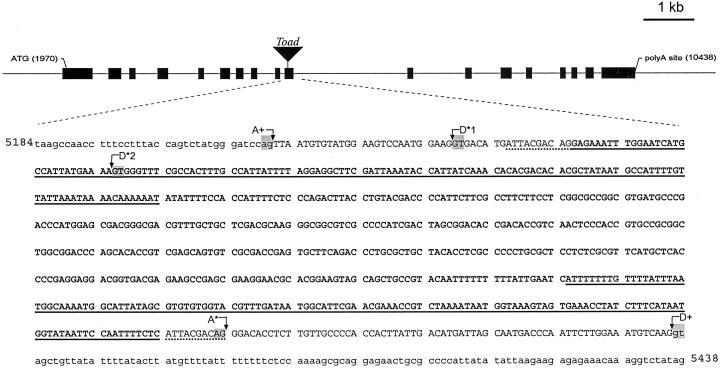
Figure 4.
Nucleotide sequence analysis of the su1-st locus. The su1-st locus contains an insertion of the 638-bp Toad sequence (shown in bold) in exon 10. Intron sequence flanking exon 10 is designated by lowercase letters, and exon 10 sequence is designated by uppercase letters. Nucleotides underlined with a dotted line indicate the 10-bp target site duplication of the host sequence. Regions underlined with a solid line indicate 138-bp TIRs within the Toad element. The wild-type acceptor site for the end of intron 9 is designated A+. The intron formed for the creation of the type-II transcript is made by joining cryptic acceptor sites D*1 to A*. This results in a deletion of 18 nt of Su1 sequence from the mature transcript and complete removal of the Toad sequence. The intron formed for the type-III transcript is produced by the use of D*2 as the donor site and A* as the acceptor site, removing most of the Toad sequence as an intron, but leaving an insertion of 30 bp in the mature mRNA. The wild-type donor site for the start of intron 10 is indicated as D+. The highly conserved GT and AG dinucleotides found at the termini of most plant introns are highlighted at the indicated splice donor/acceptor sites. The nucleotides indicated correspond to the wild-type Su1 genomic sequence (GenBank accession no. AF030882).