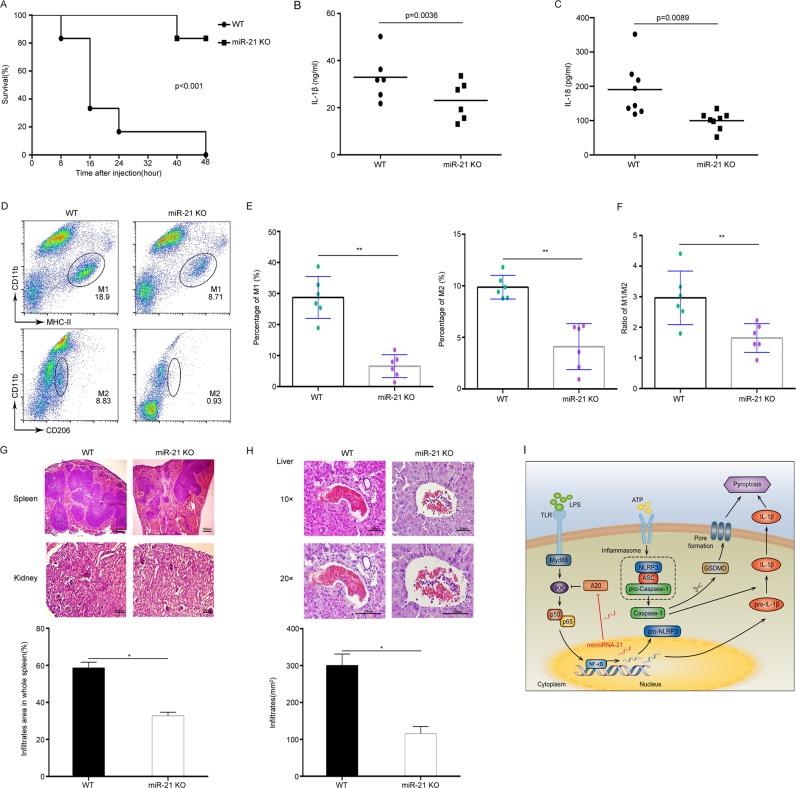
Fig. 6. miR-21 deficiency relieves LPS-induced septic shock and organ damage.
a Survival curve after LPS (35 mg/kg of body weight) was injected intraperitoneally into WT mice (n = 12) and miR-21 KO mice (n = 12). b, c Production of IL-1β and IL-18 in peritoneal lavage fluid 12 h after intraperitoneal injection of LPS (35 mg/kg of body weight) into WT mice (n = 6) and miR-21 KO mice (n = 6). d Flow-cytometry analysis of peritoneal M1 and M2 macrophages from WT and miR-21 KO mice treated with LPS. e The percentage of peritoneal M1 and M2 macrophages in WT mice (n = 6) and miR-21 KO mice (n = 6) treated with LPS. f The ratio of peritoneal M1 and M2 macrophages in WT mice (n = 6) and miR-21 KO mice (n = 6) treated with LPS. g Histological and quantitative analyses of spleens and kidneys from WT mice and miR-21 KO mice. Scale bars: 100 μm. h Histological and quantitative analyses of livers from WT mice and miR-21 KO mice. Scale bars: 200 μm. i The mechanistic model of miR-21-mediated inflammasome activation and pyroptosis