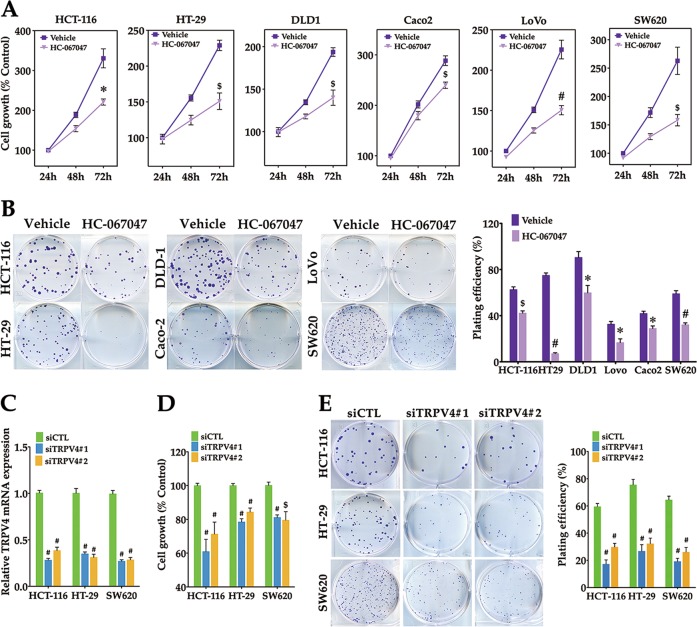
Fig. 3. Inhibition of TRPV4 activity or expression suppresses colon cancer cell growth.
a The effect of HC-067047 treatment on cell viability. The indicated colon cancer cells were treated with vehicle (0.1% DMSO) or HC-067047 (4 μΜ) and then assessed by MTT assay. b The effect of HC-067047 treatment on colony formation. The indicated colon cancer cells were seeded into six-well plates, then treated with vehicle (0.1% DMSO) or HC-067047 (4 μΜ), incubated at 37 °C for 12–14d, stained with crystal violet (0.5% w/v) and imaged. Colonies with 50 or more cells were counted. c Summary data from real-time PCR demonstrating the knockdown efficiency of TRPV4 siRNA in HCT-116, HT-29 and SW620 cells. Cells were transfected with control siRNA (siCTL), TRPV4 siRNA#1(siTRPV4#1) or TRPV4 siRNA#2 (siTRPV4#2) for 24 h. d The effect of TRPV4 knockdown on cell viability. HCT-116, HT-29 or SW620 cells were transfected as in (c), and then assessed by the MTT assay for 72 h. e The effect of TRPV4 knockdown on colony formation. HCT-116, HT-29 or SW620 cells were transfected as in (c). After 48 h transfection, cells were seeded into six-well plates, incubated and stained as in (b). All quantitative data shown represent the means ± SEM of at least three independent experiments. *P < 0.05, $P < 0.01 and #P < 0.001, versus vehicle treatment only (a, b) or the siCTL group (c, d, e)