Figure 2.
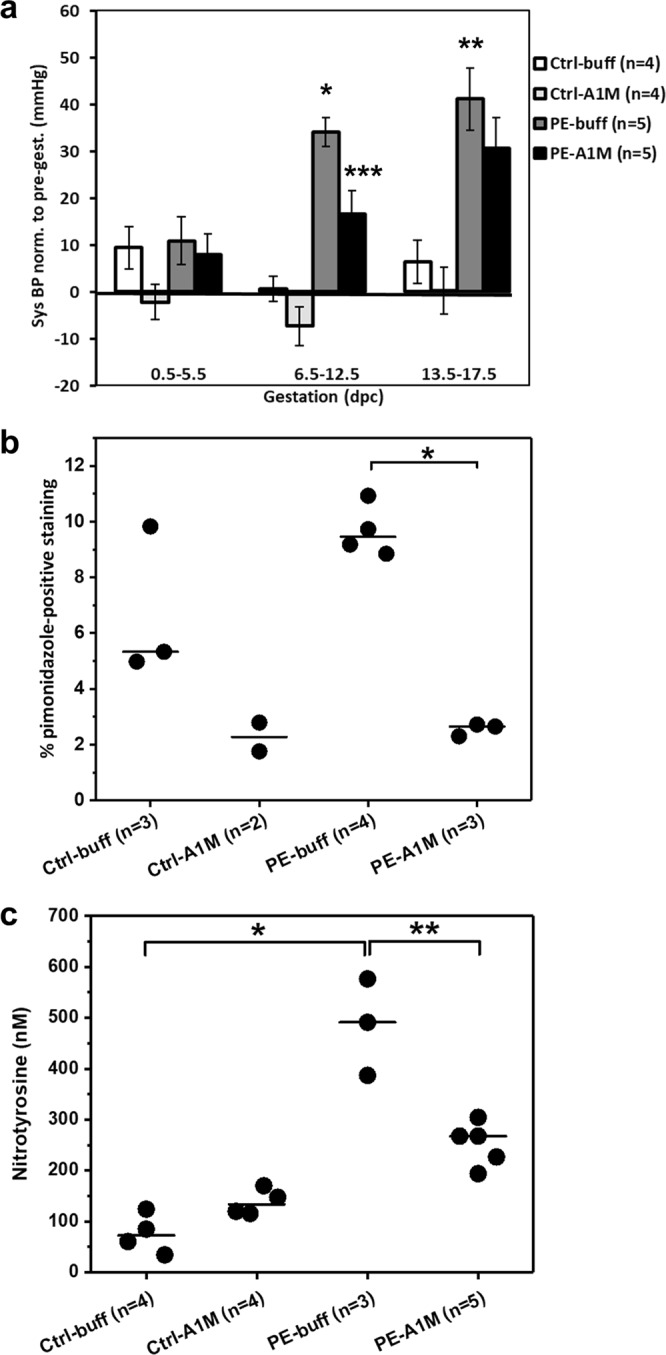
Human rA1M significantly reduces hypertension and placental hypoxia/nitrative stress levels in preeclamptic females. (a) Systolic BP measurements during early-, mid- and late pregnancy, normalised to pre-gestation pressure (mmHg). The PE-buff group displayed significantly elevated BP at mid and late gestation, compared to Ctrl-buff (*p = 5 × 10−9, **p = 5 × 10−4). Human rA1M significantly reduced BP mid-gestation, compared to PE-buff group (***p = 0.007). Shown is mean ± SEM, with 10–18 BP measurements for each gestation period and group. (b) Hypoxyprobe immunohistochemistry demonstrated a trend of higher levels of hypoxia in the junctional zone of preeclamptic placentas at 17.5 dpc, compared to controls. This was significantly reduced by rA1M treatment (PE-A1M vs PE-buff, *p < 0.0001). The line represent the median, and n = number of females analysed with three-four placentas/female. (c) Significantly elevated levels of protein nitration in the preeclamptic placentas at 17.5 dpc compared to controls (*p = 0.05), which was significantly reduced by rA1M treatment (**p = 0.04). The line represents median, and n = number of females analysed with one placenta/female.
