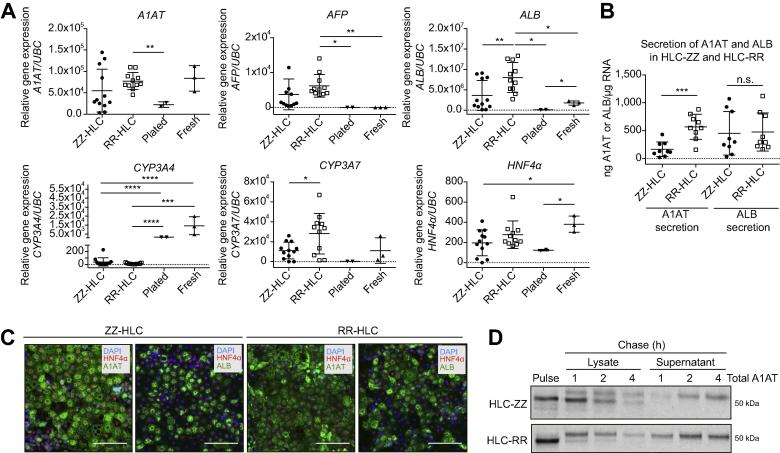
Fig. 1.
Validating a cellular platform suitable for in-depth disease characterisation. (A) qPCR analyses for the denoted genes in ZZ- (mutant, n = 12) and RR- (corrected, n = 12) HLCs vs. positive controls (plated and fresh, cryopreserved human primary hepatocytes, n = 2–3). (B) DELFIA of secreted α1-antitrypsin and albumin in ZZ- and RR-HLCs; n = 3–9. (C) Immunostaining of ZZ and RR-HLCs for HNFα, α1-antitrypsin or albumin. Scale bar: 100 μm. (D) Pulse-chase analysis: Radioactively labelled, newly-synthesised protein was tracked from the intracellular (lysate) to extracellular space (supernatant) at 1 h, 2 h and 4 h. HLCs, hepatocyte-like cells; qPCR, quantitative PCR. Statistical analyses of (A) and (B) by unpaired, parametric t test: n.s. (non-significant), *p <0.05, **p ≤0.01, ***p <0.001, ****p ≤0.0001.