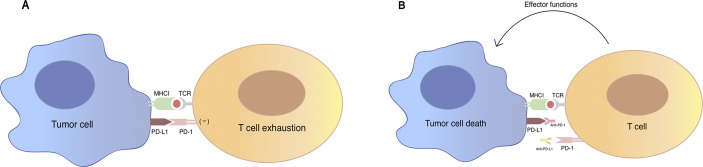
Figure 1.
An illustration of PD-1/PD-L1 mediated immune tumor response. (A) PD-1 is a co-inhibitory molecule expressed on T cell, B cells, and myeloid cells. Binding of PD-1 to its B7 family of ligands PD-L1 on tumor cells results in suppression of proliferation and immune response of T cell, which are described as the “exhaustion” state of T cell. Activation of PD-1/PD-L1 signal pathway serves as a major mechanism of immune evasion by tumor cells. (B) Antibody blockade of PD-1 and PD-L1 reverses this process and enhances anti-tumor immune response. TCR, T-cell receptor; MHC, major histocompatibility complex; PD-1: programmed cell death protein 1; PD-L1: programmed death-ligand 1.