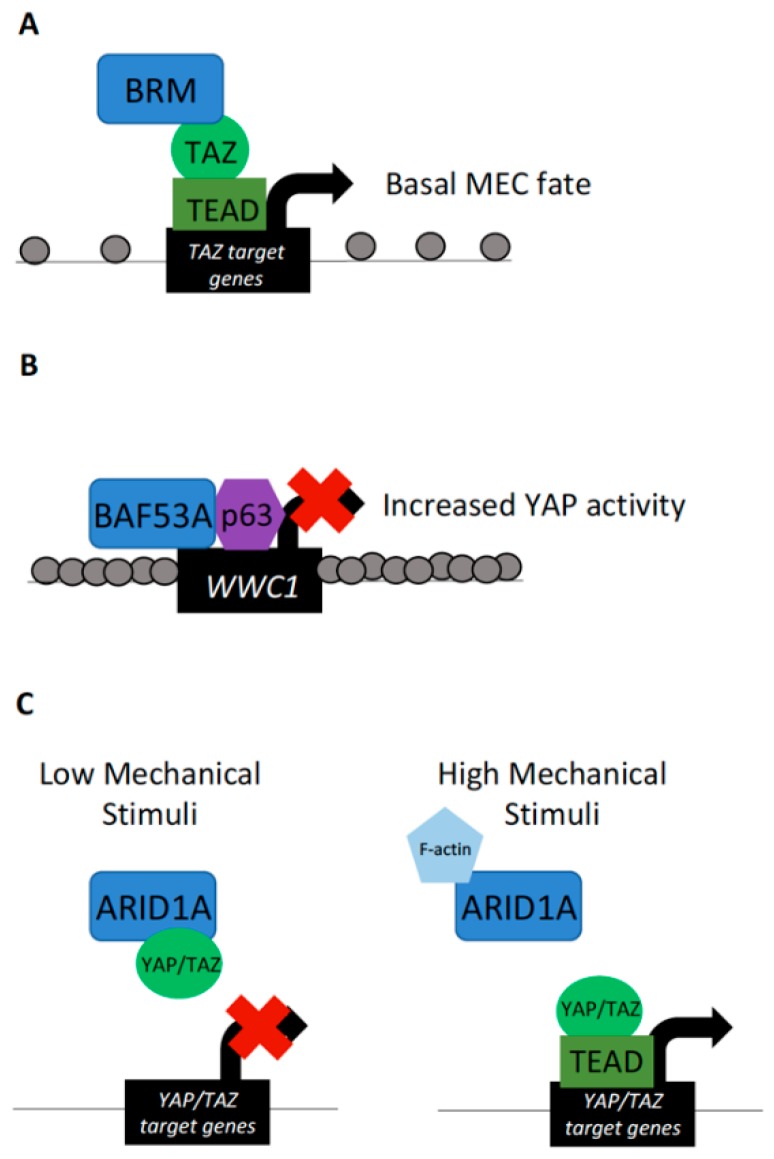
Figure 2.
YAP/TAZ interactions with the SWI/SNF complex. (A) BRM interaction with TAZ–TEAD at TAZ target loci drives transcription of genes specifying a basal cell fate in mammary epithelial cells (MECs). (B) The SWI/SNF subunit Brahma-associated factor 53a (BAF53A) interacts with p63 to inhibit the expression of WWC1/KIBRA. This results in the overactivation of YAP and is a hallmark of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC). (C) Direct interaction of the SWI/SNF subunit ARID1A with YAP/TAZ under conditions of low mechanical stimuli sequester YAP/TAZ from activating target gene expression. Under conditions of high mechanical stimuli, ARID1A itself is sequestered by nuclear F-actin, allowing YAP/TAZ to bind TEAD at target loci and induce transcription. Of note, interactions of YAP/TAZ with ARID1A does not alter chromatin accessibility at YAP/TAZ target loci. Spacing of grey dots, representing nucleosomes, represents chromatin compaction.