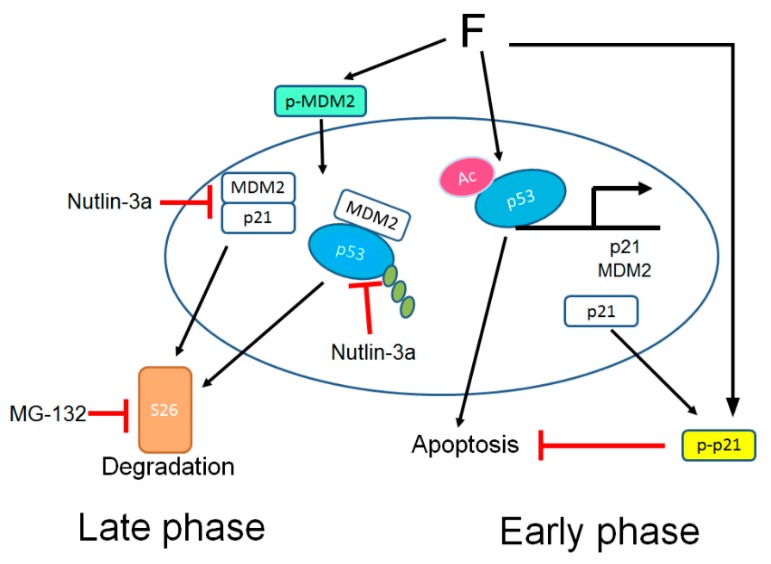
Figure 9.
Schema of MDM2-p53 and MDM2-p21 signaling in fluoride toxicity. Fluoride increases acetylated-p53 (Ac-p53) levels to upregulate transcription of Mdm2 and p21. In the early phase (1–6 h), fluoride induces phosphorylation of p21 (p-p21), which translocates p21 from the nucleus to the cytoplasm where p-p21 counteracts fluoride-induced apoptosis. Fluoride enhances MDM2-p53 and MDM2-p21 formation to promote MDM2-mediated p53 and p21 proteasomal degradation that leads to p21 and p-p21 attenuation in the late phase (24 h). Nutlin-3a inhibits MDM2-p53 and MDM2-p21 binding. Nutlin-3a or MG-132 (proteasome inhibitor) reverses fluoride-induced p21 attenuation and increases p-p21 to suppress fluoride-mediated apoptosis.