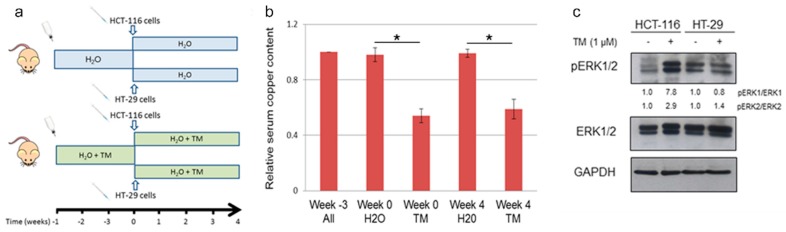
Figure 5.
Copper chelation results in reduction of serum copper content and in modulation of MAPK signaling in an in vivo human colon carcinoma xenograft model. (a) Schematic representation of animal study: animals were randomly assigned to two group (8 mice each), one receiving drinking water and the second drinking water supplemented with TM. After 3 weeks each group was divided in two subgroups: one receiving subcutaneous administration of HCT-116-luc and the second HT-29-luc. Tetrathiomolybdate administration effectively reduced serum copper content (b) and modulated ERK1/2 phosphorylation in a xenograft model of BRAFV600E-derived colorectal tumors, as assessed by immunoblot analysis (c). * (p < 0.05).