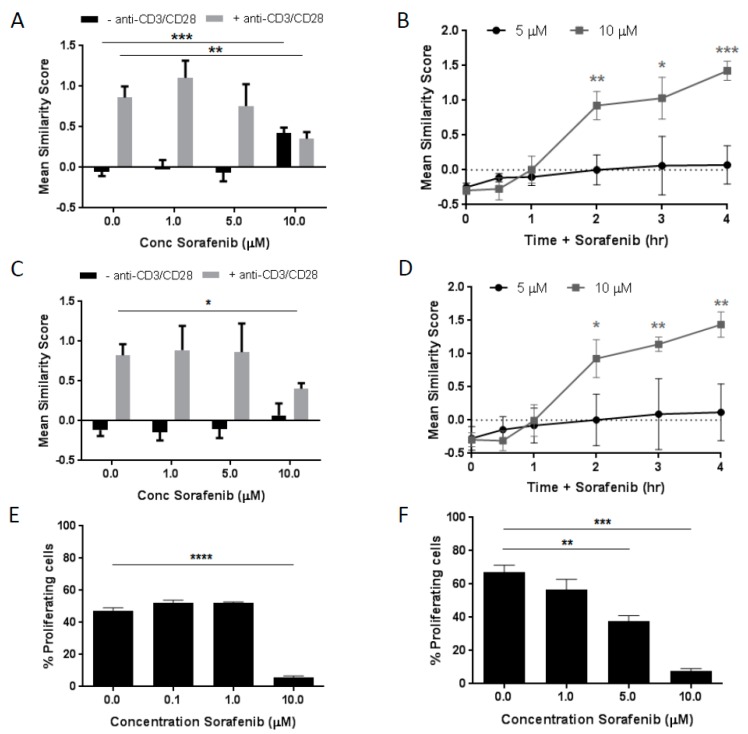
Figure 1.
Sorafenib has dose- and time-dependent effects on nuclear factor of activated T cells (NFAT) nuclear localization in T cells. (A) NFAT1 nuclear localization, measured by mean similarity score by imaging flow cytometry, exhibits a dose-dependent increase without T-cell receptor (TCR) stimulation (-anti-CD3/CD28 antibodies), and decreases with anti-CD3/CD28 antibodies in CD8+ T cells, (C) similar results observed in CD4+ T cells. (B)Mean similarity score has a time-dependent increase with high dose sorafenib (10 µM) in CD8+ T cells, (D) similar results observed in CD4+ T cells. (E) Graph shows results from one-way mixed lymphocyte reaction (MLR) in human T cells stained with carboxyfluorescein succinimidyl ester (CFSE) in the presence of increasing sorafenib concentrations. (F) Graph shows results from a similar one-way mixed lymphocyte reaction (MLR) in woodchuck T cells. All experiments are at least n = 3, * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001 by Student’s t-test.