Table 1.
Small molecule QS inhibitors. Structures, origin, working concentrations, mechanisms and effects.
| Structures of QS Inhibitors | Marine Bacterial Origins | Sources of the Bacteria | QS-Inhibitory Concentration | Anti-QS Working Mechanisms | Effects | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cyclic peptides and a linear peptide | ||||||
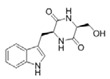 Cyclo (Trp-Ser) |
Rheinheimera aquimaris | Marine sediment surrounding the Yellow Sea in Qingdao, China | sub-MIC: 0.2 mg/mL | Probably interfere in the stability of LasR receptor | Suppress biofilm formation and QS-regulated pyocyanin and elastase activity in Pseudomonas aeruginosa | [59] |
 Cyclo-l-proline-l-tyrosine |
Bacillus cereus | Marine sediment along the Rhode Island coastline | - | Possibly inhibit Vibrio sp. LuxR | - | [37] |
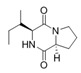
 Cyclo (l-leucyl-l-prolyl) |
Bacillus amyloliquefaciens | Mangrove rhizosphere of Palk Strait, Bay of Bengal, India | sub-MIC: 100 μg/mL | - | Inhibit QS-controlled biofilm and virulence factors (prodigiosin, extracellular polymeric substance, protease, and lipase) production in uropathogen Serratia marcescens | [60,61] |
 Cyclo (l-Pro-l-Phe) |
Marinobacter sp. | A hypersaline cyanobacterial mat from wadi Muqshin in Oman, off the Arabian Sea coast | sub-MIC: μM grade | Possibly compete with signal molecules AHLs and inhibit QS | - | [53] |
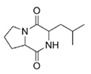
 Cyclo (l-Pro-l-isoLeu) | ||||||
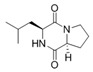 Cyclo (l-Pro-lLeu) | ||||||
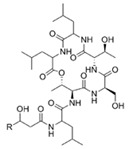 Ngercheumicin F (R = C11H21), Ngercheumicin G (R = C11H23), Ngercheumicin H (R = C13H25), Ngercheumicin I (R = C13H27) (Cyclodepsipeptides) |
Photobacterium halotolerans | Mussel surface in the tropical Pacific | 20 μg/mL | Interfere with agr QS | Reduce expression of virulence genes of hla (hemolysin) and rnaIII (an effector molecule) of agr QS in Staphylococcus aureus | [62] |
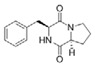
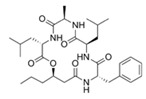 Solonamide A (Fatty acid-l-Phe- d-Leu-d-Ala-l-Leu) |
Photobacterium halotolerans | Mussel surface in the tropical Pacific | μg/mL–mg/mL | Possibly interfere with the agr QS system by competing with AIP for binding to sensor histidine kinase AgrC | Inhibit virulence gene expression of hla (hemolysin), rnaIII (an effector molecule of agr) and psmα (phenol soluble modulins) in Staphylococcus aureus, and reduce toxicity of S. aureus toward human neutrophils | [63,64] |
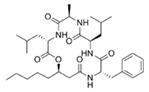 Solonamide B (Fatty acid-l-Phe- d-Leu-d-Ala-l-Leu) | ||||||
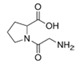 Linear dipeptide proline-glycine |
Streptomyces sp. | Marine invertebrates from the western coast of India | sub-MIC: 0.1 mg/mL | - | Inhibit QS-mediated virulence factors (swarming, pyocyanin pigmentation, biofilm formation, rhamnolipid production, and Las A) in Pseudomonas aeruginosa | [32] |
| Amides | ||||||
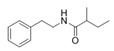 2-Methyl-N-(2′-phenylethyl) butyramide |
Oceanobacillus sp. | Marine environment | sub-MIC: μg/mL grade | - | Inhibit pyocyanin production, elastase activity and biofilm formation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa | [65] |
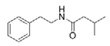 3-Methyl-N-(2′-phenylethyl)-butyramide | ||||||
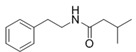
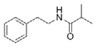 N-(2′-Phenylethyl)-isobutyramide |
Halobacillus salinus | Sea grass sample from Point Judith Salt Pond, Rhode Island | sub-MIC: μg/mL grade | Possibly compete with AHLs for receptor binding | - | [66] |
 3-Methyl-N-(2′-phenylethyl)-butyramide | ||||||
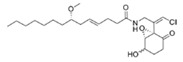 8-epi-Malyngamide C (8R) and malyngamide C (8S) |
cyanobacterium Lyngbya majuscula | Off Bush Key, Florida | μM grade | - | - | [67] |
| Fatty Acids and phenol derivatives | ||||||
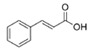 cinnamic acid |
Streptomyces sp. | Marine invertebrates from the western coast of India | sub-MIC: 0.1 mg/mL | - | Inhibit QS-mediated virulence factors (swarming, biofilm formation, LasA, pyocyanin and rhamnolipid production) in Pseudomonas aeruginosa | [32] |
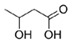 β-Hydroxy butyric acid (degradation product of PHB) |
Brevibacterium casei (sources of PHB) | Marine sponge Dendrilla nigra | 50 μg/mL (PHB) | Possibly by AHL degradation | Control biofilm formation, colonization capacity, motility and hemolysin activity of Vibrio sp. | [68] |
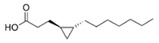 Lyngbyoic acid |
cyanobacterium Lyngbya cf. majuscula | Indian River Lagoon near Fort Pierce, Florida | μM–mM grade | Possibly inhibit lasR signaling by competing with AHL for binding LasR | Reduce pyocyanin and elastase (LasB) in Pseudomonas aeruginosa | [69] |
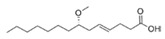 Lyngbic acid |
cyanobacterium | Corals from the Florida Keys and Belize | nM–μM grade | Compete with CAI-1 for binding to QS signal receptor CqsS | - | [70] |
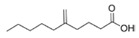 Pitinoic acid A |
cyanobacterium similar to Lyngbya sp. | A channel at the north end of Piti Bay at Guam | sub-MIC: μM–mM grade | - | Inhibit expression of QS-related virulence factor LasB (elastase) and the pyocyanin in Pseudomonas aeruginosa | [71] |
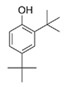 Phenol, 2,4-bis (1,1-dimethylethyl) |
Vibrio alginolyticus | Red seaweed Gracilaria gracilis from the Karankadu coastal region of Palk Bay, India | sub-MIC: μg/mL grade | - | Inhibit QS-mediated biofilm formation and virulence factor production (protease, hemolysin, lipase, prodigiosin, and extracellular polysaccharide) in the uropathogen Serratia marcescens | [72] |
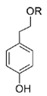 Tyrosol/tyrosol acetate (R = H or Ac) |
Oceanobacillus profundus | Caribbean soft coral Antillogorgia elisabethae | - | - | - | [49] |
| AHL analogs | ||||||
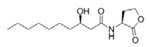 N-(3-Hydroxydecanoyl)-l-homoserine lactone |
Phaeobacter inhibens | Inner surface of an oyster shell | μM grade | Possibly by competitive inhibition of AHL-mediated QS | Inhibit virulence factor metalloprotease in Vbrio coralliilyticus | [73] |
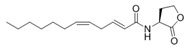 N-(Dodecanoyl-2,5-diene)-l-homoserine lactone | ||||||
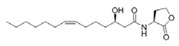 O-(3-Hydroxytetradecanoyl-7-ene)-l-homoserine lactone | ||||||
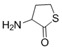 d,l-Homocysteine thiolactone |
Staphylococcus hominis | coral species (Pocillopora damicornis) in Xishan Islands, South China Sea | above 0.0625 μg/mL | Possibly compete with AHL in occupying the AHL receptor | Suppress biofilm formation and elastase production in Pseudomonas aeruginosa | [31] |
| Others | ||||||
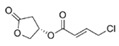 Honaucin A |
cyanobacterium Leptolyngbya crossbyana | Corals on the Hawaiian coast | μM grade | Possibly compete with AHL in occupying the AHL receptor | - | [74] |
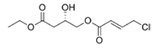 Honaucin B |
- | |||||
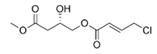 Honaucin C |
- | |||||
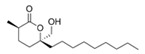 Malyngolide |
Cyanobacterium Lyngbya majuscula | Indian River Lagoon, USA | sub-MIC: 3.57–57 μM | Possibly inhibit QS by reducing or partially blocking the expression of lasR | Inhibit Las QS-dependent production of elastase by Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and possibly help the cyanobacterium to control growth of heterotrophic bacteria | [75] |
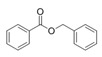 Benzyl benzoate |
Oceanobacillus sp. | Marine environment | sub-MIC: μg/mL grade | - | Inhibit pyocyanin production, elastase activity and biofilm formation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa | [65] |
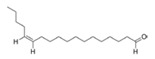 13Z-Octadecenal |
Streptomyces griseoincarnatus | Marine sponge Callyspongia sp. from Gulf of Mannar, India | - | Bind to AHL synthase LasI of Pseudomonas aeruginosa | Possibly inhibit Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm | [76] |
Note: MIC: minimum inhibitory concentration for microorganism growth.
