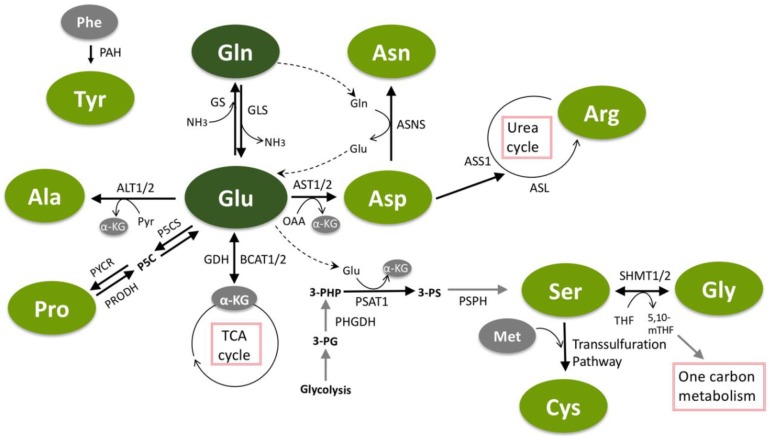
Figure 1.
The interconnected pathways of non-essential amino acids (NEAA) metabolism. Glutamine and glutamate have a central role in non-essential amino acid metabolism, and can each be used for the synthesis of other NEAAs. Glutamate can be utilized to generate alanine, aspartate, serine and proline. Aspartate is further utilized to generate asparagine (with nitrogen from glutamine) and can be used in the urea cycle to make arginine. Serine donates methyl groups for one-carbon metabolism and makes glycine in the process. Serine can also be used in the transsulfuration pathway to generate cysteine. Tyrosine is the only NEAA not directly connected to the others, as it is separately synthesized from phenylalanine. Green circles indicate non-essential amino acids. Abbreviations: Gln = glutamine; Glu = glutamate; Phe = phenylalanine; Tyr = tyrosine; Ala = alanine; Pro = proline; Asp = aspartate; Asn = asparagine; Arg = arginine; Ser = serine; Gly = glycine; Met = methionine; Cys = cysteine; α-KG = α-ketoglutarate; ALT1/2 = alanine aminotransferase 1/2; AST1/2 = aspartate aminotransferase 1/2; ASNS = asparagine synthetase; ASS1 = argininosuccinate synthetase 1; ASL = argininosuccinate lyase; BCAT1/2 = branched-chain aminotransferase 1/2; GDH = glutamate dehydrogenase; GLS = glutaminase; GS = glutamine synthetase; OAA = oxaloacetate; PAH = phenylalanine hydroxylase; PHGDH = phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase; PSAT1 = phosphoserine aminotransferase 1; PSPH = phosphoserine phosphatase; P5CS = pyrroline-5-carboxylate reductase; PRODH = proline dehydrogenase; PYCR = pyrroline-5-carboxylate reductase; Pyr = pyruvate; 3-PG = 3-phosphoglycerate; 3-PHP = 3-phosphohydroxypyruvate; 3-PS = 3-phosphoserine; SHMT1/2 = serine hydroxymethyltransferase-1/2; THF = tetrahydrofolate; 5,10-mTHF = 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate; NH3 = ammonia.