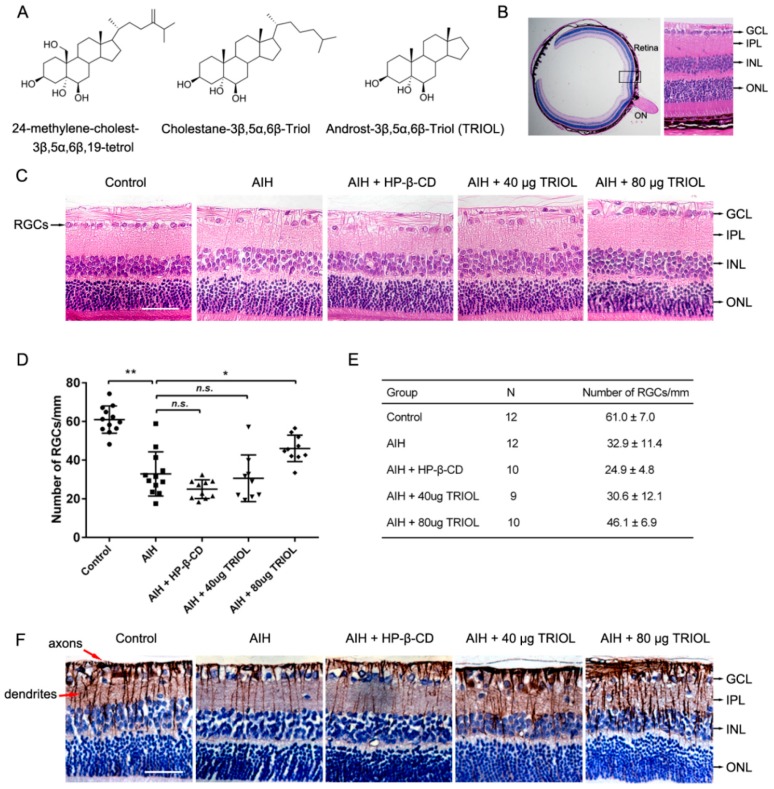
Figure 1.
Derivative 5α-androst-3β, 5α, 6β-triol (TRIOL) protects the retina from ischemic–reperfusion injury in a rat acute intraocular hypertension (AIH) model. (A) Chemical structure of 24-methylene-cholest-3β, 5α, 6β, 19-tetrol, cholestane-3β, 5α, 6β-triol, and TRIOL. (B) Schematic structural diagram of rat retina used for the analysis of retinal ganglion cells (RGCs). Black box indicates area of retina (20 μm adjacent to optic disc) used to analyze RGC survival (Optic Nerve (ON), Ganglion Cell Layer (GCL), Inner Plexiform Layer (IPL), Inner Nuclear Layer (INL), Outer Nuclear Layer (ONL)); scale bar, 400 μm. (C) Representative image of hematoxylin–eosin (HE) retina staining in different groups for analysis of RGCs in GCL. RGCs in GCL are marked with black arrows in the left panel; cell layers marked with black arrows in the right panel; scale bar, 50 μm. (D,E) Quantification of RGC numbers in GCL per mm in retina. Average RGC numbers per mm were normalized according to GCL length in each individual. N and average number are shown in E. Data are presented with mean ± SD. Statistical analysis of RGC numbers was performed using one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s post hoc analysis. N.s., no significance; *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01. (F) Representative images of immunohistochemistry (IHC) staining of Tuj1, marker of RGC axons and dendrites. Axons and dendrites are marked with red arrows in the left panel; cell layers marked with black arrows in the right panel; scale bar, 50 μm.