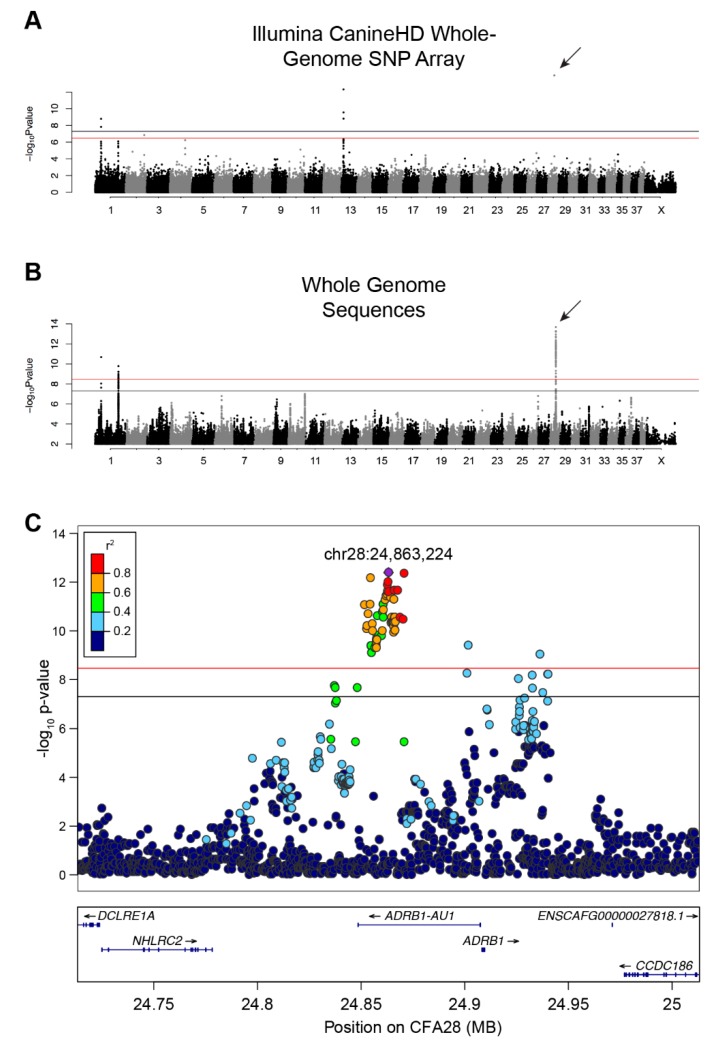
Figure 1.
GWAS identifies a strong association on CFA28 with lack of an undercoat. (A) Manhattan plot of -log10 transformed Wald p-values for the SNP association of single- versus double-coated dogs. Black horizontal line indicates genome-wide significance (5.0 × 10−8). Red line indicates Bonferroni-corrected genome-wide significance (3.3 × 10−7). Four loci surpass the significance threshold, with the most associated locus located on CFA28 and represented by a single SNP (arrow). (B) Manhattan plot of -log10 transformed Wald p-values for the WGS association of single- versus double-coated dogs. Black horizontal line indicates genome-wide significance (5.0 × 10−8). Red line indicates Bonferroni-corrected genome-wide significance (3.4 × 10-9). Three loci, two on CFA1 and one on CFA28, exceed both thresholds. Only SNPs with p-value ≤ 0.1 were included in this plot. (C) Regional Manhattan plot of CFA28 locus from the WGS GWAS. Pairwise linkage (r2) of each variant was calculated relative to the most significant variant: chr28:24,863,224 (purple). All strongly correlated variants (r2 ≥ 0.6) with significant p-values reside within the intron of an uncharacterized lncRNA.