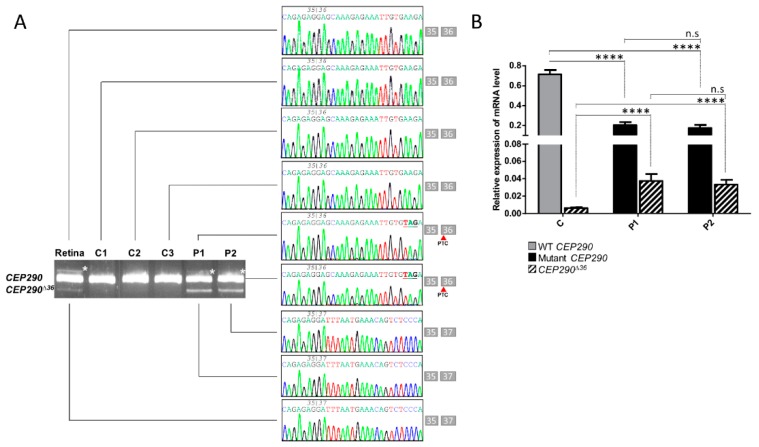
Figure 1.
Naturally occurring exclusion of CEP290 exon 36 encompassing premature stop codon. (A) Analysis of CEP290 transcript extracted from wild-type human fetal retina (Retina), control (C1–C3) and patient (P1 and P2) cell lines. Image of agarose gel and Sanger sequencing electropherograms showing amplicons produced using primer pairs surrounding mutant exon 36 and corresponding sequences. The boxes close to electropherograms summarize the exonic organization and phasing of each reverse transcription (RT)-PCR fragment. White asterisks point to heteroduplex products. Red arrows show the position of the premature termination codon (PTC) within exon 36 CEP290 isoform. (B) Relative expression levels of WT (grey bar) and mutant (black bars) full-length and skipped (CEP290∆36; hatched bars) CEP290 mRNAs in control (C represents pooled values of C1–C3) and patient (P1 and P2) fibroblasts as determined by RT-qPCR. Bars correspond to the mean ± SEM derived from ten independent experiments. **** p ≤ 0.0001, n.s = not significant.